 项目管理知识体系总览ppt课件
项目管理知识体系总览ppt课件


《项目管理知识体系总览ppt课件》由会员分享,可在线阅读,更多相关《项目管理知识体系总览ppt课件(33页珍藏版)》请在装配图网上搜索。
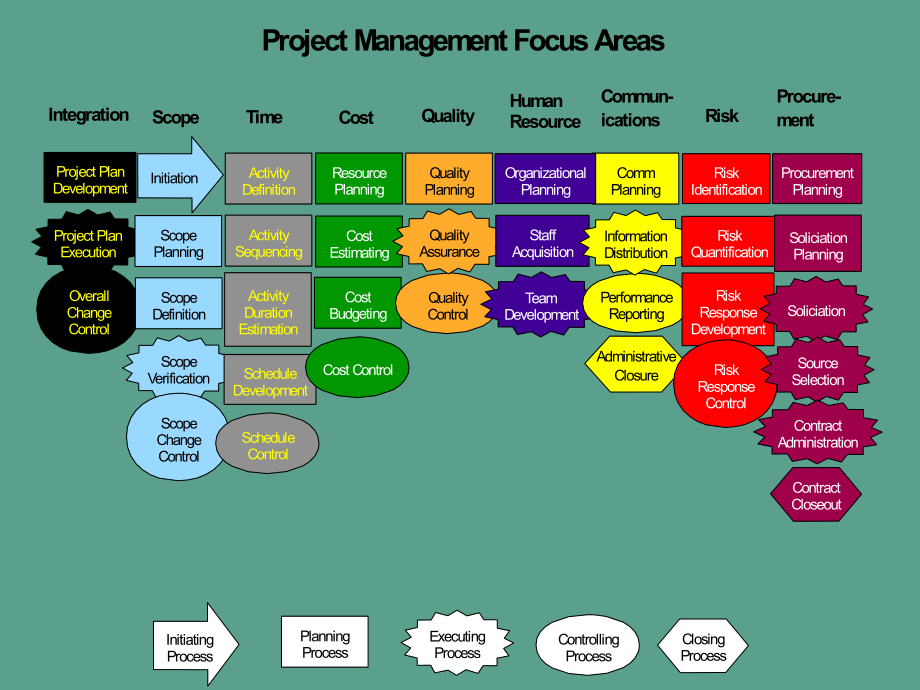
1、Project Management Focus AreasProject Plan DevelopmentOverall Change ControlProject Plan ExecutionIntegration ScopeScope VerificationScope DefinitionScope PlanningScope Change ControlTimeProcurement PlanningRisk IdentificationComm PlanningOrganizational PlanningQuality PlanningActivity DefinitionSch
2、edule ControlSchedule DevelopmentActivity Duration EstimationActivity SequencingCostQualityHuman ResourceCommun-icationsRiskProcure-mentResource PlanningCost ControlCost EstimatingCost BudgetingQuality ControlQuality AssuranceTeam DevelopmentStaff AcquisitionAdministrativeClosurePerformance Reportin
3、gInformation DistributionRisk QuantificationRisk Response DevelopmentRisk Response ControlSoliciation PlanningSoliciationSource SelectionContract AdministrationContract CloseoutInitiationExecuting ProcessControlling ProcessPlanning ProcessInitiating ProcessClosing ProcessInitiationScope PlanningScop
4、e DefinitionActivity DefinitionResource PlanningActivity SequencingActivity Duration EstimationCost EstimatingSchedule DevelopmentCost BudgetingProject Plan DevelopmentProject Plan ExecutionPerformance ReportingAdministrativeClosureOverall Change ControlContract CloseoutInitiatingPlanningExecutingCo
5、ntrollingClosingcorefacilitatingScope Change ControlSchedule ControlCost ControlQuality ControlRisk Response ControlQuality PlanningComm PlanningRisk IdentificationRisk QuantificationRisk Response DevelopmentProcurement PlanningSoliciation PlanningOrganizational PlanningStaff AcquisitionInformation
6、DistributionTeam DevelopmentQuality AssuranceScope VerificationSoliciationSource SelectionContract AdministrationInitiatingPlanningExecutingControllingClosingProject Management Processes GroupsInitiationProject Plan ExecutionPerformance ReportingAdministrativeClosureOverall Change ControlContract Cl
7、oseoutInitiatingExecutingControllingClosingProject CharterProject Mgr IDd/AssignedConstraints/AssumptionsScope PlanningScope DefinitionActivity DefinitionResource PlanningActivity SequencingActivity Duration EstimationCost EstimatingSchedule DevelopmentCost BudgetingProject Plan DevelopmentPlanningC
8、oreScope StatementSupporting DetailScope Mgmt PlanWBSActivity ListSupporting DetailWBS UpdatesProject Network DiagramActivity List UpdatesActivity Duration EstimatesBasis of EstimatesActivitly List UpdatesProject ScheduleSupporting DetailSchedule Mgmt PlanResource ReqmtsUpdatesResource RequirementsC
9、ost EstimatesSupporting DetailCost Mgmt PlanCost BaselineProject PlanSupporting DetailWork ResultsChange RequestsPerformance ReportsChange RequestsProject ArchivesFormal AcceptanceLessons LearnedContract FileFormal Acceptance&ClosureProject Management Processes GroupsScope ChangesCorrective ActionLe
10、ssons LearnedInitiatingPlanningExecutingControllingScope Change ControlSchedule ControlCost ControlQuality ControlRisk Response ControlQuality PlanningComm PlanningRisk IdentificationRisk QuantificationRisk Response DevelopmentProcurement PlanningSoliciation PlanningOrganizational PlanningStaff Acqu
11、isitionInformation DistributionTeam DevelopmentQuality AssuranceScope VerificationSoliciationSource SelectionContract AdministrationFacilitatingRevised Cost EstimatesBudget UpdatesCorrective Action PlanEstimate at CompletionLessons LearnedClosingProposalsProcurement Mgmt PlanStatement(s)of WorkProcu
12、rement DocumentsEvaluation CriteriaStatement(s)of Work UpdatesContractCorrespondenceContract ChangesPayments RequestsCommun Mgmt PlanProject RecordsPerformance ImprovementsInput to Performance AppraisalsRole/Respons AssignmentsStaffing Mgmt PlanOrganization ChartSupporting DetailProject staff assign
13、edProject team directorySources of RiskPotential RiskEventsRisk SymptomsInputs to other processesOpportunities to PursueThreats to Respond toOpportunities to IgnoreThreats to AcceptRisk Mgmt PlanInputs to other processesContingency PlansReservesContractual AgreementsCorrective Action PlanUpdates to
14、Risk Mgmt PlanQuality ImprovementAcceptance DecisionsReworkCompleted ChecklistsProcess AdjustmentsQuality ImprovementsQuality Mgmt PlanOperational DefnChecklistsInputs to other processesSchedule UpdatesCorrective ActionLessons LearnedFormal AcceptanceProject Management Processes Groups Scope Changes
15、Corrective ActionLessons LearnedInitiatingPlanningExecutingControllingScope Change ControlSchedule ControlCost ControlQuality ControlRisk Response ControlQuality PlanningComm PlanningRisk IdentificationRisk QuantificationRisk Response DevelopmentProcurement PlanningSoliciation PlanningOrganizational
16、 PlanningStaff AcquisitionInformation DistributionTeam DevelopmentQuality AssuranceScope VerificationSoliciationSource SelectionContract AdministrationFacilitatingRevised Cost EstimatesBudget UpdatesCorrective Action PlanEstimate at CompletionLessons LearnedClosingProposalsProcurement Mgmt PlanState
17、ment(s)of WorkProcurement DocumentsEvaluation CriteriaStatement(s)of Work UpdatesContractCorrespondenceContract ChangesPayments RequestsCommun Mgmt PlanProject RecordsPerformance ImprovementsInput to Performance AppraisalsRole/Respons AssignmentsStaffing Mgmt PlanOrganization ChartSupporting DetailP
18、roject staff assignedProject team directorySources of RiskPotential RiskEventsRisk SymptomsInputs to other processesOpportunities to PursueThreats to Respond toOpportunities to IgnoreThreats to AcceptRisk Mgmt PlanInputs to other processesContingency PlansReservesContractual AgreementsCorrective Act
19、ion PlanUpdates to Risk Mgmt PlanQuality ImprovementAcceptance DecisionsReworkCompleted ChecklistsProcess AdjustmentsQuality ImprovementsQuality Mgmt PlanOperational DefnChecklistsInputs to other processesSchedule UpdatesCorrective ActionLessons LearnedFormal AcceptanceProject Management Processes G
20、roups Project Life CycleCONCEPTPHASETERMINATIONCLOSE-OUTPHASEIMPLEMENTATIONEXECUTION PHASEDEVELOPMENTPLANNINGPHASEGather dataIdentify needs&alternatives Establish goals,feasibility,risk,strategyGuessitimate resourcesPresent proposalDevelop Project CharterAppoint key team membersDevelop scope baselin
21、eEstablish master plan,budget,WBS,&policies/proceduresAssess risksConfirm justification and obtain approval to proceedSet up organizationEstablish detailed technical requirementsSet up&execute work packagesDirect,monitor,and control scope,quality,time,&cost Review&accept projectTransfer responsibili
22、tyDocument&evaluate resultsRelease&redirect resources Project PrioritiesAdministrative Procedures SchedulesProject PrioritiesSchedulesAdministrative Procedures SchedulesTechnical IssuesPersonnel Resources SchedulesPersonality ConflistsPersonnel Resources Sources of ConflictProject Selection Techniqu
23、esBenefit Measurement MethodsBenefit-Cost ModelsPeer ReviewScoring ModelsMurder BoardPairwise ComparisonsConstrained Optimization Methods note these are NOT costing modelsLinear&Nonlinear programmingInteger ProgrammingDynamic ProgrammingMultiobjective ProgrammingKey INTEGRATION/SCOPE Terms80 Hour Ru
24、le=W ork PackageConfiguration Management1.develop specifications2.develop general design3.develop detailed design4.implement&test systemChange Control Board-CCBManagement by Objectivessystem of managerial leadership that defines individual managerial responsibilities interms of corporate objectives1
25、.establish unambiguous objectives2.periodically evaluate3.actMidproject Evaluation resultsidentification of problems and need for changessignificant changes in projects objectivesterminationScope Verificationoccurs at the end of each phase;formalizes acceptance of the project scope by stakeholdersDe
26、lphi Techniqueforcasting technique for gathering expert opinionK ey Form ulaeStandard D eviations1=68.3%2=95.5%3=99.7%(Six Sigm a)PER T Estim ateO ptim istic +4*M ost Likely +Pessim istic 6Sigm a=Pessim istic-O ptim istic 6D uration Am ount of W orkAvail R es*R es Productivity R atePresent Value-val
27、ue today of future cash flows PV=M (1+r)tM =am ount paym ent t years from nowr=interest rate or discount ratet-tim e periodIR R -Internal R ate of R eturn=interest rate which m ake PV costs=PV benefitsthe higher the IR R,the better the projectB enefit C ost R atio (B C R)PV R evenue PV C ostC om m u
28、nications C hannels N *(N-1)2Key FormulaeBCWP=earned valueSchedule VarianceBCWP-BCWSdif in budgeted cost of work performed&scheduledSchedule Performance IndexSPI=BCWP BCWSRatio of budgeted cost of work performed vs scheduledSchedule Variance%BCWP-BCWS BCWSschedule variance as percentage of budgeted
29、cost of work scheduledEverything about SCHEDULE is compared to WORK SCHEDULEDPERT-Program Evaluation and Review Techniquethree time estimates per activity:1.Pessimistic,2.Most Likely,3.OptomisticEvent Oriented(SLACK)amount time activity can be delayed w/o delay of projectAOA or AOL-Activity on Arrow
30、/LineCritical Path Methodemphasis on controlling cost&leaving the schedule flexibleone time estimate per activityActivity Oriented(FLOAT)amount time activity can be delayed w/o delay of projectAOA or AOL-Activity on Arrow/LineAOAActivity Sequencing by order of tasksMandatory Dependencies (HARD LOGIC
31、)Discretionary Dependencies (SOFT LOGIC or PREFERENTIAL LOGIC)External DependenciesCritical Path is longest path through the networkDummy ActivitiesAlways F-S (finish to start)Precedence Diagram Methodimproved PERT and CPM by adding LAG(waiting time)relationships to activities LEAD(accelerated time)
32、S-S,S-F,F-S,F-FAON-Activity on NodePM I believes-CPM&PERT tend to underestimate project durations by comparison to Monte Carlo analysisKey TIME TermsKey TIME Terms Crashingadd more resources to activities on the critical pathincreases COSTSFast-trackinganalyze critical path to see what activities ca
33、n be done in parallelincreases RISKResource-constrained scheduleTime-constrained schedule:absence of resources creates negative floatResponsibility Matrix:who does whatResource Spreadsheet:quantifies how much effort needed from each resourceResource Gantt chartt:shows time periods of workResource Hi
34、stogram/Resource Loading Chart:vertical bar representing total number of resources during each periodRange Estimationrange of possible results or the probability that the activity will meet the estimateHeuristic Scheduling (Rule of Thumb)trial and error;simple to use but good resultKey COST TermsWBS
35、 at lowest level=WORK PACKAGECOST ACCOUNT one level below WORK PACKAGE-used for monitoring&controllingPMI-lowest level in a project at which organizational responsibilities are assignedAnalogous Estimatingtop down estimating;usually early in project&relies on similar project outcomesParametric Estim
36、atingregression analysis-uses scatter diagram where regression line estimates average value for dependent variable (e.g.learning curve)Bottom-up Cost Estimatingdetailed estimates from project work packagesAccuracy of Estimates1.Order of Magnitude -early ballparks -25%to+75%2.Budget Estimates -initia
37、l funding -10%to+25%3.Definitive Estimates-detailed data -5%to+10%Law of Diminishing Returnsmore put in,proportionately less get outVariable vs Fixed CostsVariable-rise directly w/project size Fixed-non-recurringDirect vs Indirect CostsDirect-applies to specific project Indirect-spread acrossConting
38、ency Reservenormally included in projects cost and schedule baseline -Known RiskManagement Reserve separately planned quantity to allow for future situations impossible to predictUnknown UnknownsPerformance Measurement Baseline (PMB)Sum of Cost Account w/Contingency Reserves includedBudget Baseline
39、(BBL)PMB+Mgmt ReserveWorking CapitalCurrent Assets-Current LiabilitiesValue AnalysisCost reduction tool-anlyze design to consider whether function is required or can be done at lower costLife-Cycle Cost (LCC)total cost of ownership -cradle to grave -extends beyond projectKey COST TermsPMI-need not m
40、anage pure risk if you can insure against itBusiness RisksInsurable(pure)both gain and lossonly loss (property damage,indirect loss,legal liability,personnel)Key Risk FactorsRisk Event,Risk Probability,Amount at StakeRisk Identification1.potential sources of risks (technical nature,cost&schedule,WBS
41、,staffing plan,procurement plan)2.possible risk events (probabiity,possible outcomes,expected timing,anticipated frequency)3.risk symptomsRisk Quantificationevaluating risks&risk interactions to assess the range of possible project outcomesprimary objective-use set of structured tools to help decide
42、 which risk events warrant a responseStatistical Independencetwo events statistically independent if occurence of one not related to occurence of the otherExpected Monetary Value (EPM)Sum of the products of each Risk Events value and probabilityDecision Tree Analysiseach decision has total sum proba
43、bility of 1.0Monte Carlo Analysissuperior to PERT&CPM because it considers path convergenceImpact Analysisconsiders trade-offs:likelihood of event will occur versus severity of impact if it doesKey RISK TermsRisk Response Development1.AVOIDANCE alternative strategy2.ACCEPTANCE contingency plan (rete
44、ntion)3.MITIGATION take specific actions or deflect/transfer or use reserve (reduce)Risk Response Controlresponding to changes in risk over the course of the project1.whenever a problem or a risk arises2.whenever the project reahes a major decision point or milestoneContingency PlansWorkaroundsKey R
45、ISK TermsTypes of QUALITY Charts and/or DiagramsHISTOGRAM simple probability distributionSPC ChartStatistical Process Control;shows current capability of the processTop-Down Flowchart presents only the major or most fundamental steps in a process or projectDetailed Flowchartprovides very specific in
46、formation about a process flowWork-Flow Diagramgraphic representation of how work actually flows thru a physical spacePareto Charts data is arranged in descending order of their importance,generally bymagnitute of frequency,cost,time,or other similar parametershows frequency but not impactCause-&-Ef
47、fect Diagrams ISHIKAWA or FISHBONEgraphic representation among a list of items or factorsControl Chartsgraph that display data taken over time&computed variations of those datausually shows Upper and Lower Control Limits (natural variations in the process)Rule of Seven applies as indicator that some
48、thing is wrongAssignable(random)Causes are Special Events outside the control limits (problem/defect)Checksheets Key QUALITY TermsQuality is Free-CrosbyQuality Management involved carrying out a project through its phases with zerodeviations from project specificationsQuality Management Maturity Gri
49、d1.Uncertainty,2.Awakening,3.Enlightenment,4.Wisdom,5.CertaintyGold Platinggiving customer more than what was required-not goodFormative Quality Evaluation -Quality AuditSummative Quality Evaluation-Quality ImprovementOwnership of Qualityindividual performing the task has the ultimate responsibility
50、Cost of Qualitycost of Conformance(proactive)and cost of Non-Conformance(failure)85%of cost of quality are direct responsibility of managementKaizen continuous improvementWarusa-kagen refers to things not yet problems,but not yet quite right (Masaaki Imai)Quality should share equal priority with cos
51、t and scheduleBenchmarking-comparing your practices to those of othersJIT-just in time-inventory control approachForms of Organization1.Functional 2.Project Expeditor3.Weak Matrix4.Balanced Matirx5.Strong Matirx6.ProjectizedProject Manager Functionsjust PLOCing alongMOST IMPORTANT:PLANNING,ORGANIZIN
52、G,LEADING,CONTROLLINGAlso:Reporting,Client Relations,Logistics,Procedure Writing&AdminProject Manager Roles I Could Tell Laura DAntoni My Choice CluesIntegrator,Communication,Team Leader,Decision Maker,Climate creator/builderPM QualiicationsWORKS WELL WITH OTHERSExperience in area,supervisory experi
53、ence,education,contract admin,reflect companys position,profit oriented,qualfied negotiatorTypes of Power *PM I suggests PMs use these1.Legitimateposition in organization hierachy°reeof control over project,as mod by org2.Coercivecontrol over project and project personnel3.Reward *position in org
54、anization hierachy°reeof control over project4.Expert*personal reputation,knowledge,&experience5.Referentposition in the organizatonKey HR TermsProject Conflict SourcesHigh to Low1.Schedules 2.Project Priorities 3.Personnel Resources 4.Techical Opinions and Peformance Trade-offs 5.Administrative
55、Procedures6.Cost Objectives7.PersonalitiesConflict Management in PMI strongest to weakest1.Problem Solving/Confrontation2.Compromising3.Smoothing4.Withdrawl5.ForcingKey HR TermsTeam BuildingTeam members INDEPENDENTCONSENSUS on well-defined project goals&objectivesTeam members COMMITTED to working to
56、getherTeam is ACCOUNTABLE as unit with larger organizatonModerate level of COMPETITION and CONFLICTSymptoms of Poor TeamworkFrustrationConflict&unhealthy competitionUnproductive meetingsLack of trust or confidence in the project managerTeam Building ProcessPlan for Team BuildingNegotiate for Team Me
57、mbersOrganize teamHold kickoff meetingObtain eam member committmentsBuild communications linksConduct team building exercisesIncorporate team building activities into all project activitiesKey HR TermsMaslows Hierarchy of Needslow to highPhysiologicalSafetySocialRespect,self-respect,self-esteemSelf-
58、fulfillment and creativity (self-actualization)McGregors Theory X and Theory YX=workers are inherently LAZY,SELF-CENTERED,LACKING AMBITIONY=workers can achieve their own goals best by directing their own efforts toward organizational objectivesHerzbergs Theory of MotivationHygiene Factorspay,attitud
59、e of supervisor,working conditions poor may destroy motivation,but improvements not likely to increaseMotivators positive motivation results from an opportunity to achieve and experience self-actualizationExpectancy TheoryPeople tend to be highly producive and motivated if:1.they believe their effor
60、ts will likely lead to succesful results2.they believe they will be rewarded for their successKey HR TermsProcurement PlanningSpecificationDrawingsDelivery DatesEstimated Cost or Should Cost or Independent EstimateMake or Buy Decisionconsiders both direct and indirect costs of prospective procuremen
61、tContract Types and RisksCost Plus Percentage CPPC Reimburses allowable costs plus agreed upon percentage of est cost as profit Buyer funds all overruns Cost Plus Fixed Fee CPPF Reimburses allowable costs plus a fixed fee paid proportionately as contract progresses Ceiling on profit but NO motivatio
62、n to control costs Risk with Buyer Research&development projectsCost Plus Incentive Fee CPIF Reimburses allowable costs with predetermined bonus for superior performance Long performance periods and substantional HW development&test requirementsFixed Plus Incentive Fee FPIF Performance incentive Sha
63、red risk High-value projects over long performance periodsFirm Fixed Price FFP Lump sum Seller bears risk and had opportunity for greatest profit Definite specifications and relatively certain costsKey PROCUREMENT TermsSolicitation PlanningPreparing documents needed to support solicitationContract O
64、riginationUnilateral contract=Purchase OrderBilateral contract=Invitations to Bid-appropriate for routine items where objective is best price Request for Quotations-relatively low monetary purchases of commodity items Request for Proposals-complex/non-standard items,high monetary valueEvaluation Cri
65、teria used to rate or score proposalsunderstanding of needoverall or life-cycle costtechnical capabilitymanagement approachfinancial capacityKey PROCUREMENT TermsKey COMMUNICATIONS TermsCommunications ModesCommunicatorMessageMediumRecipientCommunications ChannelsNumber of Channels=(n*(n-1)/2Kickoff
66、Meeting -PM I believes in the value of the kickoff meetingNote-PMI emphasizes the team building possibilityes that accompany this mtgNote-PMI says the presence of communications barriers leads to increased conflictNote-PMI says the project mgr spends 90%of time in acquiring&comm infoNote-PMI believes communications flow is most difficult in matrix organization stylePMIs 6 Actions for PMs to takeBe an Effective CommunicatorBe a Communications ExpeditorAvoid Communications BlockersUse a Tight Matr
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 装配图网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。
