 AdvancedDigitalSignalProcessingcolor实用教案
AdvancedDigitalSignalProcessingcolor实用教案


《AdvancedDigitalSignalProcessingcolor实用教案》由会员分享,可在线阅读,更多相关《AdvancedDigitalSignalProcessingcolor实用教案(43页珍藏版)》请在装配图网上搜索。
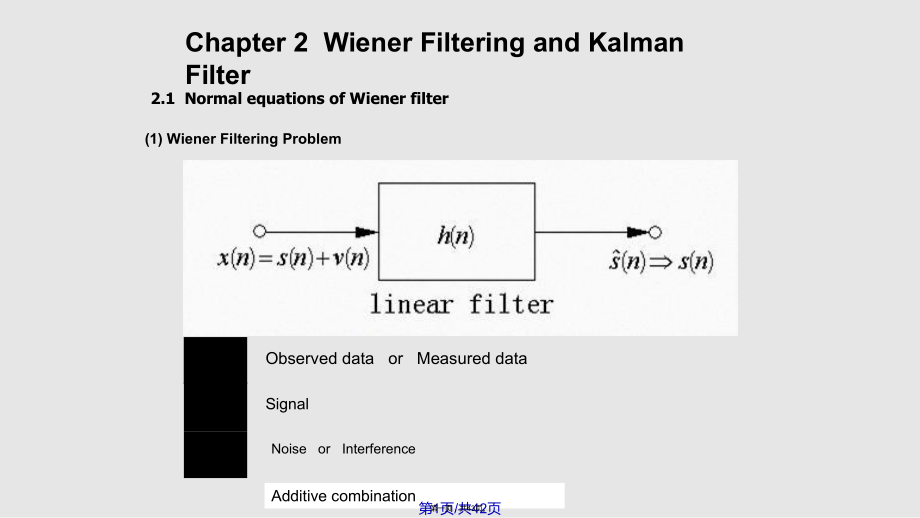
1、Chapter 2 Wiener Filtering and Kalman Filter(1) Wiener Filtering Problem ns nvObserved data or Measured dataSignal Noise or InterferenceAdditive combination 2.1 Normal equations of Wiener filter nx第1页/共42页第一页,共43页。 nhneEninxihnhnxnsimin2 nsnsneLinear estimationOptimum estimation(minimum mean-square
2、error)Estimation error第2页/共42页第二页,共43页。Smoothing Filtering Prediction niixinhns0 11npniixinhnsP-order forward one step linear prediction (LPC) 10Niixinhns第3页/共42页第三页,共43页。 121003210012000100001210NxxxxhNhNhNhhhhhhhNssss 1, 1, 0,0NninxihnsniCausality: Low diagonal matrix Wiener Filter第4页/共42页第四页,共43页
3、。(2) Orthogonal equations jjnxneEjjnxneEjhneneEjhn,0, 1, 0,022(3) normal equations (Wiener-Hopf equations) nxnsmnxnsEmRnxmnxinxEimRmimRihmRsxxxixxsx and of sequencen correlatio-cross of sequenceation autocorrel where, The Normal Equations of Causal Wiener Filter 0,0mimRihmRixxsx第5页/共42页第五页,共43页。 TTN
4、nxnxnxnNhhh11110 xh2.2 Solution of Wiener-Hopf Equations2.2.1 FIR (Finite Impulse Response) Wiener Filter第6页/共42页第六页,共43页。 1210032130122101121012101, 1, 0,10NhhhhRNRNRNRNRRRRNRRRRNRRRRNRRRRNmimRihmRxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxsxsxsxsxNixxsx nnsENRRRRsxsxsxsxxP 1210 nnERNRNRNRNRRRRNRRRRNRRRRTxxxx
5、xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxR 0321301221011210RhPRhPTTor 第7页/共42页第七页,共43页。Solution: nnnEnnsEnnnsxxxxxRPxhPRhTT1TT1opt1第8页/共42页第八页,共43页。2.2.2 Non-causal IIR (Infinite Impulse Response) Wiener FilterThe normal equations : dzzzHjnhzSzSzHzSzHzSnoptoptxxsxoptxxoptsx121 mimRihmRixxsx,第9页/共42页第九页,共43页。2.
6、2.3 Causal IIR Wiener FilterThe normal equations : 0,0mimRihmRixxsxMinimum Phase Sequence A stable and causal sequence that has a rational z-transform with all of its zeros (and poles ) inside theunit is said to be a minimum phase sequence. For example, the finite duration sequence Maaa,10is a minim
7、um phase sequence if 1,11100iMiiMiiizzzazazA第10页/共42页第十页,共43页。Minimum phase polynomial , Minimum phase systemWhy does a sequence with its all zeros inside the unit circle have minimum phase lag?Suppose is a order polynomial having only one zero inside the unit circle zFzzzA111where is a order polyno
8、mial with its all zeros outside unit circle. zA zFM1MThe zero:1zz conjugate and reciprocal relation zFzzzB11The zero:11 zz111111 1 1zzzzzz第11页/共42页第十一页,共43页。 zFzzzA111 zFzzzB11 BAzBzAzzzzzzzzzzzzz 11111111111(1) Amplitude characteristic(2) Phase lag characteristicPhase lag: AeAeAAAjAjAarg,arg BeBeBB
9、BjBjBarg,arg第12页/共42页第十二页,共43页。The phase difference : jjjjjjjeeezezeezezBA211111 ABABBA0 , 022 2 2argarg11arg argzezejj第13页/共42页第十三页,共43页。Suppose is a order polynomial having its allzero inside the unit circle. zAMMaximum phase sequenceMaximum phase PolynomialMaximum phase systemM2sequences having t
10、he same amplitude characteristic but different phases characteristics.第14页/共42页第十四页,共43页。2. Spectral Factorization Theorem The rational power spectrum of a real stationary random signal can be factored into a product of theform3. Model of Wide-Sense Stationary Random SignalsynthesisanalysisThe white
11、ning filter s.polynomial phase minimum areboth and , where12zDzNzDzNzBzBzBzSxx第15页/共42页第十五页,共43页。Proof for the spectral factorization theorem:Symmetry of the power spectrum of a real stationary random signal: 1zSzSxxxxReal zero:Complex zero:iz1iz 1izizReal zeroComplex zero第16页/共42页第十六页,共43页。In order
12、 to that is stable and causal , is also stable and causal, and both must be minimum phase polynomials. zB zDzNzB zNzDzB1Causal and stable zB1All poles ( all zeros of ) are inside the unit circle zDAll poles ( all zeros of )are inside the unit circle zN zD zNAll zeros of and are inside the unit circl
13、e. zN zD第17页/共42页第十七页,共43页。(1) Any regular process may be realized as the output of a causal and stable filter that is driven by white noise having a variance of . This is known as the innovations representation of the process. (model)(2) If is filtered with the inverse filter , then the output is w
14、hite noise with a variance of . The formation of this white noise process is called the innovations process .(3) Since and are related by an invertible transformation, either process may be derived from each other. Therefore, they both contain the same information.2 nx zB12 n nx第18页/共42页第十八页,共43页。 0
15、,0mimRihmRixxsx 0iinxihnhnxns nnx2 ng zSzGnunRngmmgimigmRmmRmimRigmRssisis2220220110, where0,a white noise with variance A causal IIR Wiener filter with impulse response 4. causal IIR Wiener filter (with a white noise as input)Stable, Causal. The poles inside the unit circle.第19页/共42页第十九页,共43页。5. A
16、input with rational power spectrum polynomils phase minimum areboth and ,12zDzNzDzNzBzBzBzSxxSpectral factorized theoremis causal and optimal zG zSzGs21 iinxifn zGzBzHc1第20页/共42页第二十页,共43页。 121zBzSzBzHsxc 12111 zBzSzGzBzSzSzFzSmRmfimRifinxifmnsEnmnsEmRsxsxsxssxisxis第21页/共42页第二十一页,共43页。Computational s
17、teps Product factorization (spectral factorization theorem)(2) Sum factorization of 111zBzSzBzSzBzSsxsxsx(3) Compute the system 121zBzSzBzHsxc(4) Compute the impulse response(5) Compute the minimum mean-square error 12zBzBzSxx第22页/共42页第二十二页,共43页。2.3 Mean-Square Error of Wiener Filter 0 2minesRnsneEn
18、snsneEneEn zSzHzSzSzSzSzSdzzxSjRndzzzSjmRxsoptsss ssssssescuesesmceses 210 211.min1 dzzzSzHzSjncuxsoptss1.min 21第23页/共42页第二十三页,共43页。Why is Wiener filter optimal? vvssssoptvvssssxxssoptSSSHzSzSzSzSzSzH 0 01 0optvvoptssoptvvHSHSHS第24页/共42页第二十四页,共43页。2.4 Computation of Causal Wiener FilterGiven: signal
19、 model measurement model 1 ,1anwnasns 1 ,cnvncsnxAssumptions: 00, 0, 1 iwnvEisnvERivnvEininQiwnwEninini RzSQzSvvwwWhite noises第25页/共42页第二十五页,共43页。Solution: RazazQczSzSczSzSazazcQzcSzSzcSzSzSazazQzSnvncsnxnwnasnsvvssvcsxxsssvssvcsssxss11 11 11 , 1122112第26页/共42页第二十六页,共43页。(1) Product factorization (s
20、pectral factorization theorem) 1,11, 111111 1111121221222212fazfzzBzBzBazazzRaQcaRzRaQcaRRaQcRazazQczSxxzffzffffzfzzRaQcaRzRaQcaRRaQc212221222122221111111111第27页/共42页第二十七页,共43页。RaQcaRffRacQf22222211110,22PPcRRPaPQRicatti Equation(2) Sum factorization fzazcQfzazazazcQzBzSzGsx111111111 methodexpansion
21、 fraction partial (2) residueby method formulainversion (1) ?zGPCRPaQcaRf22221222or vfaRaf第28页/共42页第二十八页,共43页。(1) Inversion formula method 1111azfacQzG(2) Partial fraction methodfzzafcQf11fzBz1 1111azfacQzG circle)unit theinside (poles 0,1 ,11sRe21.111nafacQazfzazcQdzzzGjngncunn 111111 111azafcQazAf
22、zazcQzG第29页/共42页第二十九页,共43页。(3) Compute the system function of the causal IIR filter gain Wiener the111111 111111 1211211122facQGfzGfzfacQazfacQazfzzGzBzHc第30页/共42页第三十页,共43页。Another method for computing causal IIR Wiener filter 122221 )3(1or )2(solution positive ) 1 (fzGzHcGafPcRaRfPcRcPGPPcRRPaPQc第3
23、1页/共42页第三十一页,共43页。PcRaRf2afPPcRRPaPQ122PcRcPcPfacQG2221PcR22cGaPcRPacaPcRaRf1222 PcRcPG2cGaf1第32页/共42页第三十二页,共43页。222or vfaRaf第33页/共42页第三十三页,共43页。2.5 Scale Kalman Filter 1 ,1 ,nnxnnsnnsns nxGnnsfnnsn11 1111 nnsacnxGnnsannsnThe first prediction:The second prediction:Innovation:NoImage111nnsnnsa1111nns
24、acnnscnnx 111nnsacnxnnxnxncGaf1第34页/共42页第三十四页,共43页。The optimal gain (Kalman gain) 1min 1212222nnsnsneneEnPcnPRcnPcRncPGGnnsnsEneEnnnPrediction error powerPrediction error第35页/共42页第三十五页,共43页。The minimum mean square error nPnPcGnPcGnPnnsnsEneEnnn1 22Prediction error power QnanP122wQ第36页/共42页第三十六页,共43页
25、。Computational steps QnanP12 nPcRncPGn2 nPcGnn 1 1111 nnsacnxGnnsannsnInitiation 11,110,001sGPs第37页/共42页第三十七页,共43页。2.6 Vector Kalmin Filter2.6.1 Signal Vector and Data Vector qinwnsansiiii, 2, 1 , 1 nnnaaanwnwnwnnsnsnsnqTqTqwAssAws1000000 212121第38页/共42页第三十八页,共43页。 nnnbanwnnsnsnnsnsnwnbsnasnsnsnsnsn
26、snsnwnbsnasnswAssAws101 0 11111 ,212112211121第39页/共42页第三十九页,共43页。 nnncccnvnvnvnnxnxnxnqkkinvnscnxkTkTkiiiivCsxCvx000000000)( , 2, 1 212121第40页/共42页第四十页,共43页。2.6.2 Derivation of Vector Kalman Filter nnnnnnvAsxwAss1TTTBAABAAAABBAbabaaabba122Scale arithmetic matrix arithmetic 111111nnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnnn
27、nnnnnnnnnsCAxGsAsPCGIRCPCCPGQAAP1TTT第41页/共42页第四十一页,共43页。谢谢大家(dji)观赏!第42页/共42页第四十二页,共43页。NoImage内容(nirng)总结Chapter 2 Wiener Filtering and Kalman Filter。(minimum mean-square error)。(2) Orthogonal equations。(3) normal equations (Wiener-Hopf equations)。(1) Amplitude characteristic。(2) Sum factorization。谢谢大家(dji)观赏第四十三页,共43页。
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 装配图网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。
