 生物化学:Chapter 5-5 Protein function
生物化学:Chapter 5-5 Protein function


《生物化学:Chapter 5-5 Protein function》由会员分享,可在线阅读,更多相关《生物化学:Chapter 5-5 Protein function(22页珍藏版)》请在装配图网上搜索。
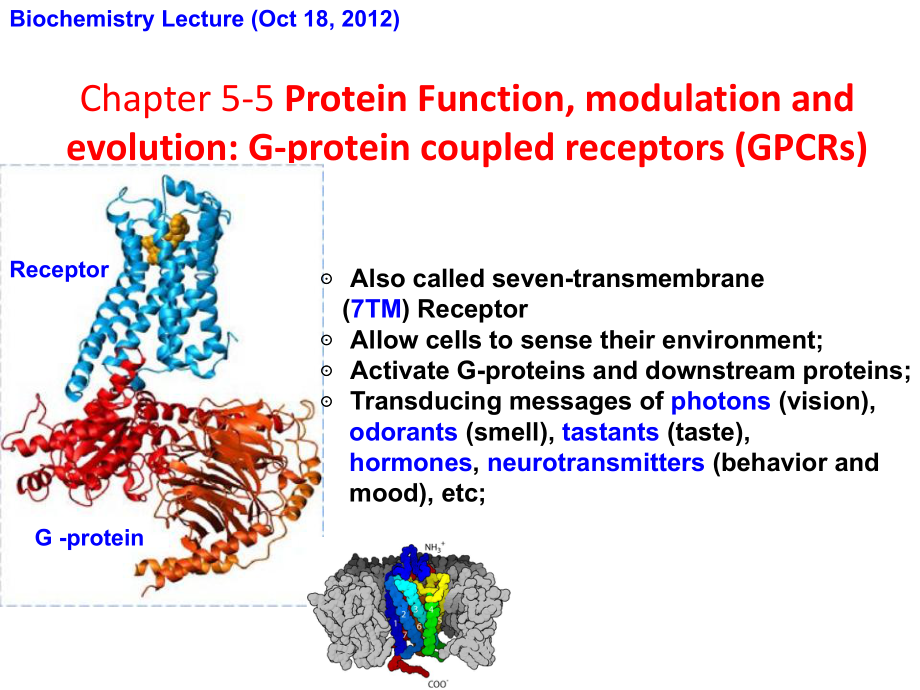
1、Biochemistry Lecture (Oct 18, 2012)Chapter 5-5 Protein Function, modulation and evolution: G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) Also called seven-transmembrane (7TM) Receptor Allow cells to sense their environment; Activate G-proteins and downstream proteins; Transducing messages of photons (vision),
2、 odorants (smell), tastants (taste), hormones, neurotransmitters (behavior and mood), etc;G -proteinReceptorEpinephrine, a catecholamine prepares an animal to “fight or flight”.Nerve signals and hormones from the brain alert the body. The adrenal gland releases stress hormones into the bloodstream.
3、Cells throughout the body sense that something is happening via their receptors and respond accordingly.Epinephrine is also produced in the brain!GPCR is a superfamily, with b b2 adrenergic receptor (b b2AR) being a model system Human genome encodes about 1,000 GPCRs; Being targets of approximately
4、30% of all modern medicinal drugs! Ligand binding to GPCR activate the G-proteins, which modulate further downstream proteins and the physiological states of the cells.G protein cycle for b b2ARConformational rearrangementsof GPCRGs heterotrimerDissociation of a a & bc bc subunitsEffector proteinsAc
5、tivated adenylyl cyclaseCa2+channelsHydrolysis of GTPSecond messengersActivated GPCREpinephrine(adrenaline)GGGProlonged exposure to ligands desensitizes GPCR Dissociation of ligand Phosphorylation and binding of b b-arrestinIt is now commonly accepted that GPCR function as homo-oligomers in living c
6、ellsHistory of understanding the structure of G-protein coupled receptorExample of rhodopsinoligomeroligomericGPCRGPCRGPCRGPCRrhodopsinrhodopsinrhodopsinmonomericmonomerPark et al., 20041905196219762000Fotiadis et al., (2006) Structure of the rhodopsin dimer: a working model for G-protein-coupled re
7、ceptors,Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 16:252259Earl W. Sutherland, Jr.for his discoveries concerning the mechanisms of the action of hormones1971 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine1994 Nobel Prize in Physiology or MedicineAlfred G. GilmanMartin Rodbellfor their discovery of G-proteins an
8、d the role of these proteins in signal transduction in cells2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry Brian K. KobilkaRobert J. Lefkowitzfor studies of G-proteincoupled receptorsAquaporins form hydrophilic transmembrane water channelsOriginally isolated as a 28 kDa contaminant of the Rh blood group antigen from
9、 red blood cells, abundant in kidney tubes.(Nobel, 2003(Nobel, 2003)The potassium channel in bacteria is a homotetramer membrane proteinThe structure explains the exact mechanism by which potassium channel selectivity occurs. The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1988“For the determination of the three-dimen
10、sional structure of a photosynthetic reaction center.” Dr Johann DeisenhoferUniversity of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, USAProfessor Robert HuberMax-Planck-Institutfr Biochemie,Martinsried, FRGDr Hartmut MichelMax-Planck-Institutfr Biophysik,Frankfurt/Main, FRG Structure of thephotosynt
11、hetic reaction center in purple Bacteria.A electron pathwas proposed.e-e-e-Periplasmic sideCytoplasmic sideCyt c2Cyt bc1complexMML LC CH H The hormone epinephrine was found to act through the second messenger cAMP in activating glycogen degradation in liver cells (Sutherland, 1958) A heat stable fac
12、tor (cAMP) is produced in the presence of epinephrine and glucagon in liver homogenate. This factor then stimulates the formation of liver phosphorylase (rate-limiting for glycogenolysis in a fraction of the homogenate where the hormones are not present. EpinephrineCyclic AMPProteins interacting wit
13、h the GTP (not ATP) found to needed to activate adenylyl cyclase (Gilman and Rodbell, 1960s). Concept of signal transduction proposed as a means of coupling information between signal-activated receptor (discriminator) and regulation of adenylate cyclase (signal amplifier); G-protein to be the trans
14、ducer.Radio-ligands or agonists used to detect GPCR receptors on specific cell membrane preparations (1970s, Lefkowitz) Radioactive iodine (125I) labeled adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) specifically binds to adrenal extract and stimulates adenylyl cyclase. Similar radiolabeled (3H) -Adrenergic Re
15、ceptors agonists were used to characterize the epinephrine receptors in activating adenylyl cyclase activity.Lefkowitz et al (1970) ACTH receptors in the adrenal: specific binding of ACTH-125I and its relation to adenylyl cyclase. PNAS, 65:745-752. Lefkowitz et al (1974) Stereospecific (3H)(minus) -
16、alprenolol binding sites, beta -adrenergic receptors and adenylate cyclase. BBRC, 60:703-709. Coupling between ligand and G-protein binding events observed (1980, Lefkowitz) A ternary complex model, involving the extracellular ligand (agonist), transmembrane GPCR and intracellular G-protein, was pro
17、posed to serve as the active signalling unit. Allosteric coupling being mutual: binding of agonist increases the affinity for the G protein and vice versa.Limbird LE, Gill DM, Lefkowitz RL (1980) Agonist-promoted coupling of the beta-adrenergic receptor with the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein
18、 of the adenylate cyclase system. PNAS,77:775. De Lean A, Stadel JM, Lefkowitz RL (1980) A ternary complex model explains the agonist -specific binding properties and the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta -adrenergic receptor. JBC, 255:7108. G protein and receptor aredifferent entities!The receptors pu
19、rified and reconstituted into phospholipid vesicle Affinity chromatography using specific ligand-conjugated resins: b2-adrenoceptor, being a single polypeptide chain 60 kDa. A hormone-responsive adenylate cyclase system reconstituted from purified receptor and Gs and the catalytic moiety of adenylyl
20、 cyclase. Stimulated by agonists but inhibited by antagonists. Molecular details for the signaling process could be examined!Caron MG, Srinivasan Y, Pitha J, Kociolek K, Lefkowitz RJ (1979) Affinity chromatography of the beta-adrenergic receptor. JBC, 254:2923 -2927. Cerione, R.A.et al. (1984 ) Reco
21、nstitution of a hormone-sensitiveadenylate cyclase system. The pure beta-adrenergic receptor and guanine nucleotide regulatory protein confer hormone responsiveness on the resolved catalytic unit. JBC. 259, 9979 9982Genes encoding epinephrine receptor cloned Homology with rhodopsin revealed. Seven t
22、ransmembrane helices predicted.Dixon RA et al (1986) Cloning of the gene and cDNA for mammalian beta-adrenergic receptor: primary structure and membrane topology. Nature 321:75 -79. RhodopsinEpinephrine receptorMembrane-spanning a a-helices can be predicted from amino acid sequences via hydropathy p
23、lottingHydropathy index is calculatedFor successive segments (windows) of a given size, from 7 to 20 residues;For a window of 7 residues, the indices for residues 1 to 7, 2 to 8, 3 to 9, and so on, are plotted for the middle residue in each Window residue 4 for residues 1 to 7, etc);A region with ab
24、out 20 residues of high hydropathy index ispresumed to be a transmembrane segment.Each amino acid is assigned a relative hydrophobicity indexStructure of the b b2 adrenergicreceptorGs protein complex with agonist bound determined (2011, Kobilka) Activation mechanism: small change around the ligand p
25、ropagates, mainly via TM6 and 5, into a large structural transition on the inside, opening of a deep hydrophobic cleft for G to penetrate into. Rasmussen SG et al (2011) Crystal structure of the human beta2 adrenergic receptor -Gs protein complex. Nature 477: 549-555. GPCRGsNanobodyT4 lysozymeStabil
26、ized;Kept GTP/GDPfreeStudying the structure and fucntion of membrane proteins is still very challenging Biogenesis and quality control: folding, translocation, assembly, degradation, etc. Structure, Function, mechanism and regulation: differences with the soluble proteins and roles of the lipids. Evolution: special requirements for the different types of orgnanisms.
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 装配图网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。
