 exoytosis and endocytosis课件
exoytosis and endocytosis课件


《exoytosis and endocytosis课件》由会员分享,可在线阅读,更多相关《exoytosis and endocytosis课件(47页珍藏版)》请在装配图网上搜索。
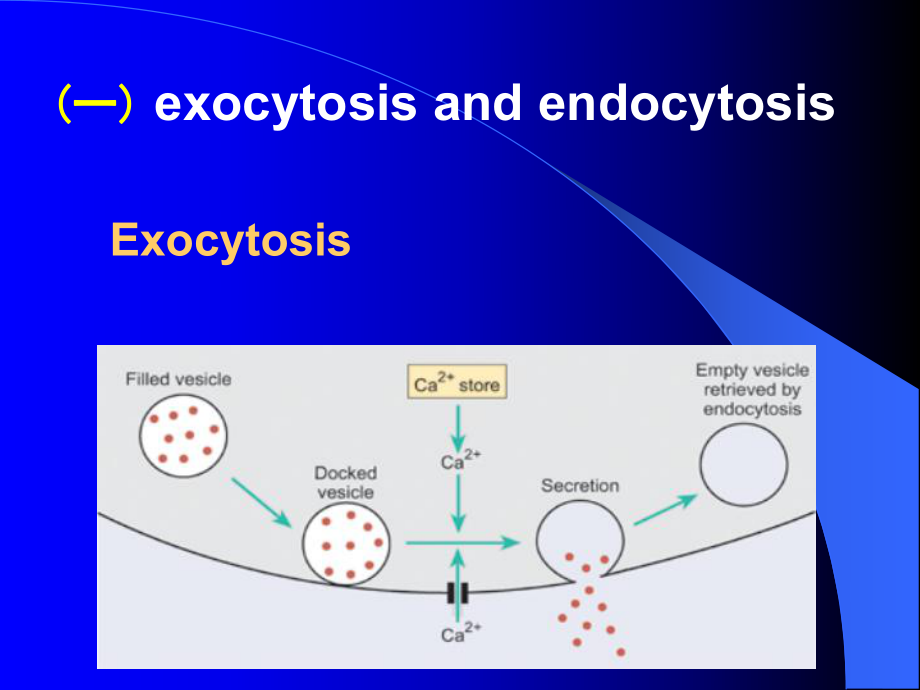
1、( (一一) ) exocytosis and endocytosis Exocytosis Endocytosis:(1)Phagocytosis (2)pinocytosis:fluid-phase endocytosis,Receptor-mediated endocytosisReceptor-mediated endocytosis Section 2 Membrane Potentials and Action PotentialsElectrical potential exist across the membranes of essential all cells of th
2、e body.Some cells, such as neuron and muscle cells, are “excitable” that is, capable of generation of electrochemical impulses at their membranes. In most cases, these impulses can be used to transmit signals along the membranes.( (一一) ) Resting potential,RP Basic Electrophysiological Terms Polariza
3、tion: a state in which membrane is polarized at rest, negative inside and positive outside.Depolarization: It means the membrane potential becomes less negative than the resting potential (close to zero). Hyperpolarization: It means that the membrane potential is more negative than the resting level
4、.Repolarization: It means restoration of normal polarization state of membrane. It is a process in which the membrane potential returns toward from depolarized level to the normal resting membrane value. Na+( (+50+70mV) )ion equilibrium potential K+ K+( (-90-100mV) )Leakage of K+ and Na+ through the
5、 nerve membraneNernst Equation EK=60 log ( (mV) ) K+ o K+ iOrigin of the normal resting membrane potential.1.Contribution of the potassium diffusion potential Potassium ions, concentrated inside the cell tend to move outward down their concentration gradient through nongated potassium channels lNern
6、st potential for the inside of membrane is +61mv(Na+): minute diffusion of sodium ions through the K+-Na+ leak channels.Origin of the normal resting membrane potential2.Contribution of sodium diffusion through the nerve membrane EMF (millivolts)= -61 log CNa+i p Na+ + CK+i p K+ + Ccl-o p cl- CNa+o p
7、 Na+ + CK+o p K+ + Ccl-i p cl-So, Goldman equation=-86mv (potential for the inside of membrane )Calculation of the Diffusion Potential When the Membrane Is Permeable to Several Different Ions the permeability of the membrane (P) to each ion, the concentrations (C) of the respective ions on the insid
8、e (i) and outside (o) of the membrane. Thus, the following formula, called the Goldman equation, or the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation, gives the calculated membrane potential on the inside of the membrane when two univalent positive ions, sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+), and one univalent negative i
9、on, chloride (Cl-), are involved. Origin of the normal resting membrane potential3.Contribution of the Na+-k+ pumpNa+-K+ pump: -4mvSo, the net membrane potential= -90mvConclusionThe formation of resting potential depends on:1. Concentration difference of K+ across the membrane2. Permeability of Na+
10、and K+ during the resting state3. Na+-K+ pumpDefinition of Resting Potential (RP)A potential difference across the cell membrane at the rest stage or when the cell is not stimulated.Property:1) It is constant or stable2) It is negative inside relative to the outside3) Resting potentials are differen
11、t in different cells. eg: muscle cell: -90mv, Red blood cell: -10mvFactors that affect resting potential1)Difference of K+ ion concentration across the membrane2)Permeability of the membrane to Na+ and K+.3)Action of Na+ pumpDifinition:Action potential is a rapid, reversible, and conductive change o
12、f the membrane potential after the cell is stimulated.Nerve signals are transmitted by action potentials. II Action PotentialSuccessive stage: Resting stage: The membrane is said to be “polarized “ during this stage because of the -90mv negative membrane potential that is present.Depolarization stag
13、e: The membrane suddenly becomes very permeable to sodium ions.Repolarization stage: the sodium channels begin to close and the potassium channels open more than normal.Re-establish the RP.Action Potential Sequence Depolarization stage Voltage-gated Na+ Channels open and Na+ rushes into the cellActi
14、on Potential SequenceDepolarization stage At about +30 mV, Sodium channels close, but now, voltage-gated potassium channels open, causing an outflow of potassium, down its electrochemical gradientAction Potential Sequence The Sodium Potassium Pump is left to clean up the messBasic Electrophysiologic
15、al Terms II:Excitability: The ability of the cell to generate the action potential.Excitable cells: Cells that generate action potential during excitation. So in excitable cells (muscle, nerve, secretory cells), the action potential is the marker of excitation. Some scholars even suggest that in exc
16、itable cells, action potential is identical to the excitation.Stimulus: It is a sudden change of the (internal or external) environmental condition of the cell. It includes physical and chemical stimulus. The electrical stimulus is often used for the physiological research. Threshold (intensity): th
17、e lowest or minimal intensity of stimulus to elicit an action potential(Three factors of the stimulation: intensity, duration, rate of intensity change)Types of stimulus:Threshold stimulus: The stimulus with the intensity equal to thresholdSubthreshold stimulus: The stimulus with the intensity weake
18、r than the thresholdSuprathreshold stimulus: The stimulus with the intensity greater than the threshold.Action Potential Summary 1. Reduction in membrane potential (depolarization) to threshold level leads to opening of Na+ channels, allowing Na+ to enter the cell2. Interior becomes positive3. The N
19、a+ channels then close automatically followed by a period of inactivation.4.Next K+ channels open, K+ leaves the cell and the interior again becomes negative.Process lasts about 1/1000th of a second.Properties of the Action Potential(1)“All or none” phenomenonA threshold or suprathreshold stimulus a
20、pplied to a single nerve fiber always initiate the same action potential with constant amplitude, time course and propagation velocity.(2) Propagation传播(3) Transmitted in both direction in a nerve fiber(4) Refractory periodThreshold Potential-Threshold for initiation of the action potentialThreshold
21、 potential plays a key role in the genesis of action potential.Threshold potential is a critical membrane potential level at which an action potential can occur.Why can all the Na+ channel open at the threshold potential? It is dependent on the gating property of the voltage-gated Na+ channels.The v
22、alue of threshold potential of most excitable cell membrane is about 15 to 20 mV less negative than the resting potential.The threshold stimulus is just strong enough to depolarize the membrane to the threshold potential level, therefore it can cause an action potential.Electrophysiological Method t
23、o Record Membrane Potentialfor their discoveries concerning the function of single ion channels in cellsThe Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (1991)Erwin NeherBert SakmannCytoplasmIon channelsGiga-sealGlassmicroelectrodeSuction1 mPatch clamp recordingCell Membrane100 ms4 pAClosedOpenSingle chann
24、el record III Local ResponseDefinition:Local response is a small change in membrane potential caused by a subthreshold stimulus Role of the Local Potential1)Facilitate the cell. This means it increase excitability of the stimulated cell2)Cause the cell to excite once it is summed to reach the thresh
25、old potentialIV. Propagation of the Action Potential1.Direction of propagation: in all direction2.All-or-nothing principle: Once an action potential has been elicited at any point on the membrane of a normal fiber, the depolarization process travels over the entire membrane if conditions are right,
26、or it does not travel at all if conditions are not right. This is called the all-or-nothing principleMyelinated neuron of the central nervous systemSaltatory conduction: The action potential jumps from node to nodeThe pattern of conduction in the myelinated nerve fiber from node to node is called “s
27、altatory conduction”. It is of value for two reasons: 1)very fast:5 to 50-fold2) conserves energy for the axon: only nodes depolarize, allowing 100times less loss of ions and require little metabolism for reestablish the sodium and potassium concentration differences.Mollusk: Calamary: axon diameter
28、: 1mmV Excitationthe process of eliciting the action potential1.Threshold Stimulation and Excitability2.Change of Excitability after the ExcitationThe period during which a second action potential cannot be elicited, even with a strong stimulus, is called the absolute refractory period. Slide 3 of 28
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 装配图网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。
