 英语选修课语法简要讲解(精品)
英语选修课语法简要讲解(精品)


《英语选修课语法简要讲解(精品)》由会员分享,可在线阅读,更多相关《英语选修课语法简要讲解(精品)(10页珍藏版)》请在装配图网上搜索。
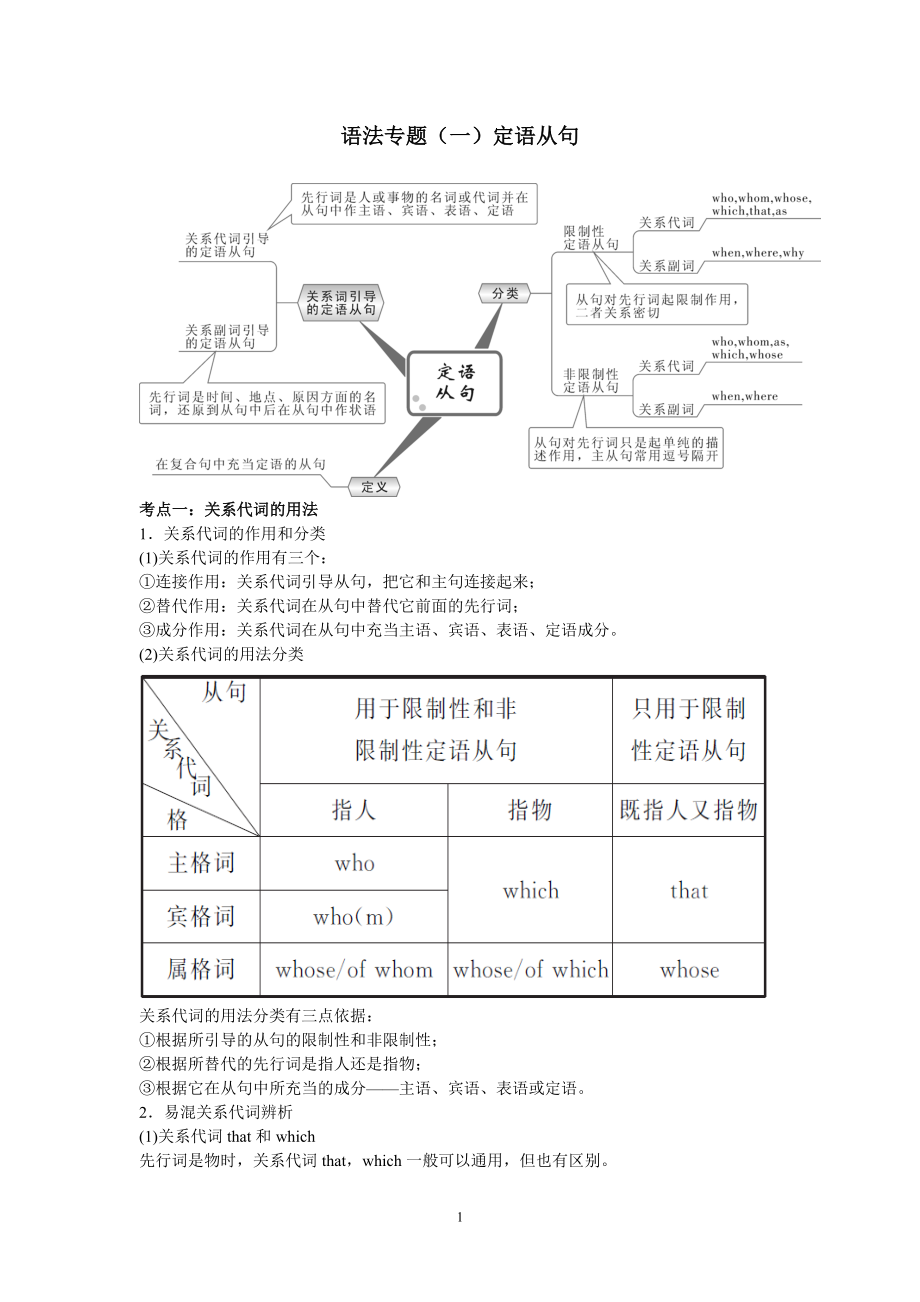
1、语法专题(一)定语从句考点一:关系代词的用法1关系代词的作用和分类(1)关系代词的作用有三个:连接作用:关系代词引导从句,把它和主句连接起来;替代作用:关系代词在从句中替代它前面的先行词;成分作用:关系代词在从句中充当主语、宾语、表语、定语成分。(2)关系代词的用法分类关系代词的用法分类有三点依据:根据所引导的从句的限制性和非限制性;根据所替代的先行词是指人还是指物;根据它在从句中所充当的成分主语、宾语、表语或定语。2易混关系代词辨析(1)关系代词that和which先行词是物时,关系代词that,which一般可以通用,但也有区别。1)只能用that的情况先行词为指物的不定代词(all, n
2、othing, the one, much等)或被不定代词修饰时,如:You can take any seat that is free.Tell us all that you know.先行词是序数词或被序数词修饰时,如:That is the first composition that Ive written in English.先行词是形容词最高级或被形容词最高级修饰时,如:This is the best way that has been used against pollution.当人和物同为先行词时,如:Everyone wants to see the spacesh
3、ip and the spaceman that made the flight around the earth.关系代词在从句中作表语时,如:He is no longer the man (that) he used to be.先行词被the only,the very修饰时,如:That is the very pen (that) I am looking for.当先行词是which时,如:Which of the two cows that you keep produces more milk?先行词为the way/the time/the moment/the first
4、 time/the last time等名词时,如:I dont like the way(that)he talks.This is the third time(that)he has been late this week.注意:此时that为关系副词,若先行词没有被the first/the last修饰时,用that和when均可,如:The time (that)/(when) I saw you was 8:00.(2)关系代词as和whichas既可指人又可指物,主要用于as;asas;the sameas;suchas等结构中,在从句中作主语、宾语或表语。引导的从句可位于句中
5、、句首、句末。如:As is reported in the newspaper,talks between the two countries are making progress.Mary was late for school,as is often the case.as引导非限制性定语从句,修饰整个句子,而which不仅可修饰整个句子还可以修饰单个名词。如:The meeting,which was held in the park,was a success.The meeting was a success,as was expected.(3)who和that先行词是人时,关
6、系代词可用who(m),that引导定语从句,但下列情况一般用who,而不用that。先行词是one,ones,anyone或anybody,those时,如:Anyone who breaks the law should be punished.一个句子中带有两个定语从句,其中一个的关系词是that时,如:The student that won the first prize is the monitor who speaks English best in our class.在there be句型中和非限制性句型中,如:There is a person who wants to s
7、ee you.I met an old classmate yesterday, who is now a manager of a big company.(4)who,whom和whosewho指人,在定语从句中作主语或宾语,whom指人,在定语从句中作宾语。作宾语时who和whom一般可通用,但直接放在介词之后时,一般只用whom,不可用who。如:Take your problem to the person who you think can help you.She is the girl (who/whom) I will go to Shanghai with.She is t
8、he girl with whom I will go to Shanghai.whose既可指人,也可指物,在从句中作定语。如:George Orwell,whose real name was Eric Arthur,wrote many political novels.The librarian refused to accept the book,whose cover was gone when it was returned.3关系词的省略作宾语的关系代词可以省略,但前面不能有介词。如:This is the man(who/whom/that) we have talked a
9、bout.口语中,关系副词可以省略(尤其是先行词为time,way,reason等时)。如:This is the reason (why)I did it.I dont know the time (that) he arrived.4限制性和非限制性定语从句限制性定语从句起修饰限制的作用,是主句不可缺少的一部分,与先行词无逗号隔开,翻泽成中文常译成前置定语。如:Those who want to go,sign their names on the paper.那些想去的人把他们的名字签在纸上。5定语从句中的主谓一致关系词在定语从句中作主语时,从句的谓语动词要与先行词保持一致。如:I,wh
10、o am your friend,will leave for Beijing tomorrow.which和as指代一个句子时,从句谓语动词用单数。如:Mary is often late for class,which makes our teacher very unhappy.6“介词/介词短语which/whom”中介词的选择关系代词前面的介词使用是根据与名词前面的动词搭配关系和介词的搭配关系及句子结构上的需要而定的。如:Well never forget the day on which we went camping.(on the day)The woman to whom w
11、e spoke is from the USA. (speak to sb.)His glasses,without which he was(who was not)like a blind man, fell to the ground and broke.(由句意决定)考点二:关系副词的用法1当先行词在定语从句中作状语时,要用关系副词。其中when表示时间的介词(如:in,at,during等)which;where表示地点的介词(如:in,at,on,under等)which;whyforwhich。如:I still remember the day when I first cam
12、e to Beijing. (whenon which)Can you tell me the office where he works? (wherein which)Do you know the reason why he is absent? (whyfor which)2高考对关系副词where的考查高考试题中对于where的考查趋于复杂,从先行词由“明显的地点”转为“地点的模糊化”。事实上,对于where这个词,考生不能只理解为表示地点。当先行词表示某人/物的处境,或某事所发展的阶段,或表达某事的某个方面时都可用where这个关系副词。如:The accident had rea
13、ched to a point where both their parents are to be called in.事情发展到如此程度,不得不请双方家长来一趟了。试比较下面的句子:Do you still remember the days that/which we spent in Qingdao?你还记得我们一起在青岛度过的日子吗?Do you still remember the days when we spent the summer holidays in Qingdao?你还记得我们在青岛过暑假的日子吗?在句中,定语从句中缺宾语,因此须用关系代词that/which来引导
14、从句,而在句中,定语从句中不缺主语,也不缺宾语,因此须用关系副词when来引导从句。2定语从句与其他句式的比较It is such a heavy box that he cant lift it.(状语从句)It is such a heavy box as he cant lift.(定语从句)Is this factory the one in which/where we lived three years ago?(定语从句)Is this factory where we lived three years ago?(表语从句)As is known to the world, M
15、ark Twain is a great American writer.(定语从句)It is known to the world that Mark Twain is a great American writer.(主语从句)That Mark Twain is a great American writer is known to the world.(主语从句)We dont understand the problem why this is the best choice.(同位语从句)The reason that he gave was not right.(定语从句)Sh
16、e did all she could to help him.(定语从句)She is not the girl she used to be.(定语从句)She did what she could to help him.(宾语从句)She is not what she used to be.(表语从句)由以上例句可以看出,分清定语从句与其他复合句的关键是要掌握先行词及其后的关系词,要看其是否在从句中作成分,是否有意义。3注意way和time后接定语从句的情况(1)当先行词是way意为“方式、方法”时,在定语从句作状语,引导定语从句的关系词有下列三种形式。如:(2)先行词是time时,
17、若time作“次数”讲时,应用关系代词that引导定语从句,that可省略;若time作“一段时间”讲时,应用关系副词when或介词at/duringwhich引导定语从句。如:This is the second time(that) the President has visited the country.这是总统第二次访问那个国家。I could hardly remember how many times (that) Ive failed.我几乎记不清我已失败多少次了。This was at a time when/during which there were no radios
18、,no telephones or no TV sets.这是一段没有收音机,没有电话,没有电视机的时间。语法专题(二)时态和语态一、动词时态的用法1一般现在时(1)由连词if,unless,however等引导的时间(条件、让步)状语从句,需用一般现在时表将来。However much advice you give him,he will do exactly what he wants.(2)安排或计划要做的动作(有时间状语)限于begin,come,leave,go,arrive等一类动词。I arrive in Beijing at 300 pm. tomorrow.2一般过去时过去
19、一段时间内经常或反复发生的行为,常与every day,often,sometimes等时间状语连用。I used to play football when I was young.3一般将来时(1)willdo表示将来的动作或状态,常与一些表示将来的时间状语连用;或表示事物的固有属性或必然趋势。Fish will die without water.注意:临时决定做某事,只能用此时态。The lights in the classroom are still on.Sorry,Ill go and turn them off.(2)be going todo表示即将发生的或最近打算进行的事
20、。此外还表示根据现在的迹象,对未来进行推测。Look at the clouds.It is going to rain.(3)be about todo表示即将发生的动作,意为“正要;很快,马上”。后面一般不跟具体的时间状语,但是可以由when连接一个并列句。We are about to leave.(4)be todo表示事先商定、安排或准备要做的事情;还表示可能性、必要、责任、义务、禁止等。She is to get married next month.(5)用现在进行时表示将来。表示位置转移的动词(go,come,leave,start,arrive等),可用现在进行时表示将来。U
21、ncle Wang is coming.4现在进行时表示说话人对主语的行为表示赞叹或厌恶等感情色彩,常与always,constantly,continually等副词连用。She is always asking the same question.5现在完成时现在完成时表示从过去某一时刻开始一直延续到现在的动作或状态,或者还要延续下去,句中常有since,for,yet,already等表示一段时间的状语。Great changes have taken place in China since 1980.6过去进行时过去进行时表示在过去某个时刻正在进行的动作或存在的过去某个阶段正在做的事
22、情。He was reading an interesting book this time yesterday.7过去完成时(1)表示在过去某个时刻前已经发生的动作或存在的状态,或者从过去某个时刻开始一直延续到过去另一时刻的动作或状态。My teacher had taught in that school for ten years before she came here.(2)表示希望或打算的动词(如hope,want,expect,think,suppose,plan,mean,intend等)的过去完成时,后接不定式to do时,表示未曾实现的愿望或打算,即“本来希望或打算做某事(
23、但却没做)”。I had planned to send him a Christmas card,but I forgot to do so.(3)用于下列特殊句型中:hardly/scarcely/barely had.done.when.;no sooner had.done.than.。从句中用一般过去时,表示“刚刚就”。Hardly had I opened the door when he told me.It/That/This was the first/second.timethat从句。that从句要用过去完成时态。It was the second time he had
24、 been out with her.8过去将来时过去将来时表示从过去的观点来预计以后要发生的动作或存在的状态,这种时态常用于宾语从句中,主句常是一般过去时。He always said that he would study hard at that time.二、被动语态的用法1不知道动作的执行者是谁或难以说明时常用被动语态。Street lights are often turned on at six in winter.2当动作的承受者比起动作的执行者来说更能引起人们的关注而需要加以强调时,要用被动语态。This kind of bicycle is not sold in our
25、shop.3含有双宾语的句子,主动句中的间接宾语或者直接宾语都可变为被动语态中的主语,另一个保留不变。变为主语的若是主动句中的直接宾语,间接宾语前则需加介词to或for。The pianist gave the pupils(间接宾语) some advice (直接宾语)The pupils were given some advice by the pianist.Some advice was given to the pupils by the pianist.4在主动语态句中,动词make,have,let,see,watch,hear,feel等后接动词不定式作宾语补足语时,动词不
26、定式不加to。但变成被动语态时后面的不定式都需加上to。The boss made them work ten hours a day.They were made to work ten hours a day by the boss.三、注意事项1现在进行时用法注意点(1)状态性动词不用进行时态。(2)进行时态和副词always,forever等连用时,往往带有一定的感情色彩,如赞扬、批评、不满、抱怨等。2过去进行时与一般过去时的区别过去进行时表示动作的未完成性、持续性,着眼于动作的过程;一般过去时表示动作的完成,即动作发生过,且已结束,着眼于结果。She was writing a re
27、port last night and I dont know if she has finished it.(表示昨晚一直在写)She wrote a report last night.(表示昨晚写了,并且写好了)3语态(1)动词sell,write,read等与well,smoothly,easily等连用时,说明主语内在的“性能”、“特点”,用主动表示被动。(2)表示状态特征的连系动词如smell,taste,feel,sound,look,prove等无被动语态,用主动形式表示被动意义。(3)不及物动词及一些固定短语不能用被动语态:come up,run out,give out等。
28、(4)以被动的形式表主动意义:有些动词devote,surprise,seat,hide,station,dress等,由于能接反身代词,因此,可用被动形式表主动意义。语法专题(三)情态动词一、can和could的用法1表示能力Her mother can speak French.2表示客观可能性Anybody can make mistakes.3表示许可(多用于口语)Can I go now?4表示惊异、怀疑、不相信的态度(主要用于否定句、疑问句或感叹句中)How can you be so careless!5can的特殊用法can but只有;cant but不得不;cant.too
29、再怎样也不为过,越越好。I can but wait.I cant but wait.You cant be too patient to the customers.二、may和might的用法1表示允许、请求May I watch TV now?Yes,you may.(Yes,please.)No,you mustnt.(No,youd better not.)2表示可能性(主要用于陈述句、肯定或否定句,疑问句用can代替)The story may not be true.3表示祝愿(不用might)May you succeed!4may/might as well最好还是You m
30、ight as well do it now.5may/might well很可能He may well be late for class.三、must,have to和ought to的用法1must(1)must表示“必须,应该,一定要”。强调主观看法,只有现在时形式,否定式是must not(mustnt)。must开头的问句,其否定回答要用neednt或dont have to代替。(2)must表示必然的结果。All men must die.(3)must还可表示主语固执、偏要做他人不希望做的事。It cant help;he must do that.2have to着重客观需
31、要,能用于更多时态(过去时或将来时)。He will have to be there before ten.3ought to表示义务和责任,“应该”,比should语气要强。You ought to take care of yourself.四、need和dare的用法1need表示“需要,必要”,只能用于否定句和疑问句。在肯定句中,常用must和have to代替。2dare表示“敢”,通常用于否定句、疑问句和条件状语从句中。Dare you go home alone at eleven in the evening?3need和dare的特殊用法(1)need表“需要”时,可用wa
32、nt,require代替。The desk needs to be repaired./The desk needs repairing.(2)dare作实义动词时,在肯定句中要接to,在疑问句和否定句中to可省去。He dares to catch a snake.五、will和would的用法1will(1)表示请求、建议,常用于第二人称。Will you please go with me?(2)表示意愿、决定、允许。I will never do that again.(3)表示习惯性动作或某种倾向,“总是,惯于”,通常用于第三人称。Fish will die out of water
33、.2would(1)表示请求、建议,比will委婉,指现在时间,多用于第二人称。Would you like a cup of tea?(2)表示过去习惯性动作或某种倾向。We would play badminton on Sundays.六、shall和should的用法1shall(1)用于第一、三人称,在问句中表示征求对方意见或请求。(2)用于第二、三人称表示命令或威胁。You shall do as your father says.2should(1)表示责任、义务,意为“应该”。(2)表示惊讶语气,意为“竟然”。You should wear slippers in class.
34、(3)用于条件句,表示“假如,万一”,省去if,should可提至句首。Should you be late,apologize to the teacher.七、“情态动词have done”的用法1must have done sth.;can(could) have done sth.(1)must have done sth.表示对过去已经发生的事情的有把握的推测,意思是“想必、准是、一定做了某事”,只用在肯定句中。It must have rained last night,for the ground is wet.(2)can(could) have done sth.表示对过去
35、发生的动作的怀疑和不肯定,通常用在否定句和疑问句中。He cant have forgotten it.2neednt have done sth.;didnt need to do sth.(1)neednt have done sth.表示已完成不需要完成的动作。You neednt have waken me up.I dont have to go to work today.(2)didnt need to do sth.表示没有必要做而实际上也没有做某事。I didnt need to clean the windows.My brother did it.3may/might h
36、ave done sth.may/might have done sth.表示对过去已发生的动作的推测,意为“也许/或许已经”。Im not sure.He might have said so at the conference.4should have done sth.should have done sth.表示本来应该做某事而实际上未做。You should have told him about it.5had better have done sth.;would rather have done sth.;would like/love to have done sth.(1)
37、had better have done sth.表示事后的建议,含轻微责备的口吻,意为“当时做了某事就好了”,其否定形式had better not have done sth.表达相反的含义。(2)would rather have done sth.表示“宁愿当时做某事”,其否定形式would rather not have done sth.表达相反的含义,两者都含有“后悔”之意。I would rather have taken his advice.(3)would like/love to have done sth.表示过去愿意做某事,但未做成。I would love to
38、have gone to the party last night,but I had to work extra hours to finish my report.语法专题(四)名词性从句在句子中起名词作用的句子叫名词性从句。 名词性从句的功能相当于名词词组,它在复合句中能担任主语、宾语、表语、同位语等,因此根据它在句中不同的语法功能,名词性从句又可分别称为主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句和同位语从句。考点一whether 与ifwhether与if 在作“是否”的意思讲时在下列情况下一般只能用whether,不能用if:1引导主语从句并在句首时。Whether the meeting wil
39、l be held tomorrow has not been decided yet.2引导表语从句和同位语从句时。We should discuss carefully the question whether we can finish it on time.3引导从句作介词宾语时。It all depends on whether they will lend us the money.4从句后有“or not”时。I didnt know whether or not he had arrived in Beijing.5后接动词不定式时。I dont know whether to
40、 go to the party.考点二that,what与which1that 引导名词性从句时,在从句中不充当任何句子成分,只起连接作用,也没有任何含义;that 引导的宾语从句一般不作介词的宾语(介词but,except,besides,in除外)。That he failed the exam made me surprised.(主语从句,that不充当从句成分)He is a good student except that he is a little careless.2what引导名词性从句时,其意义为“的人/物/数目等”,在从句中充当主语、宾语、表语或定语。作主语、宾语和表
41、语时what可以分解成“定语从句的先行词关系代词”,即常说的“先行词that”。Our income is now double what it was ten years ago.(what 指“的数目”)You will know what side effect the medicine brings about.(作定语,意思为“什么样的”)He lives in what we call“spring city”(表示“的地方”)He lives in the place that we call “spring city”You dont know what good studen
42、ts they are.(表示“多么”,此为感叹句用于宾语从句中)3which 引导名词性从句,其意义为“哪一个”,可指人也可指物,是在已知的具体的人、事、物当中进行选择;引导定语从句时,只能当关系代词,在从句中作主语或宾语,且只能指物。Tell me which book you like better,the red one or the blue one?I will buy the book which you choose for you.4A is to B what C is to D“A对于B 就像C对于D 一样”。Air is to us what water is to f
43、ish.空气对于我们就像水对于鱼一样。考点三whoever,who与no matter who1whoever有两个作用,一是相当于anyone who,引导名词性从句,可以理解为who引导的定语从句修饰anyone,因此表达的主体为“任何人”;二是相当于no matter who,引导让步状语从句。Whoever comes late should say sorry to our teacher.(是“人”应该道歉)2who引导名词性从句时,有疑问语气,突出表达“谁”这一件事。引导定语从句时代替先行词在从句中作主语或宾语。Who came late yesterday was unknow
44、n.(是“谁迟到”这件事不知道,而不是不认识这个人)3no matter who只引导让步状语从句。No matter who you are,youre welcome here.考点四“疑问词 ever”和“no matter疑问词”1“疑问词ever”可引导名词性从句,在从句中要充当一定的成分。还可引导让步状语从句。Whoever breaks the rule must be punished.However late he comes back,his wife will wait for him.2“no matter疑问词”只能引导让步状语从句。No matter who bre
45、aks the rule,he must be punished.考点五 that引导宾语从句时的省略宾语从句中的连接词that通常可以省略,但在以下几种情况中that不能省略:1当从句前有插入语时,that不可省略。We hope,on the contrary,that he will stay at home with us.2当一个句子有两个或多个并列宾语从句时,引导第二个和以后的宾语从句中的that不能省略。He said he was wrong and that he would say sorry to me.3当that作介词宾语时,that不可省略。The reason l
46、ies in that she works harder than the others.4由it作形式宾语时,that引导的宾语从句中,that不可省略。I think it impossible that he can finish the task in such a short time.考点六it作形式主语的常见句型1It is名词(no wonder,an honor,a good thing,a pity,no surprise等)从句。It is no surprise that we will win the match.2It is形容词(obvious,true,natu
47、ral,surprising,good,funny,possible,likely,certain等) 从句。It is certain that he will come.3Itbe过去分词(said,reported,thought,expected,decided,announced 等)从句。It is said that Mr Smith has arrived.考点七doubt 后面的从句doubt用于肯定句时,其后的宾语从句用whether/if引导,同位语从句用whether引导;用于否定句时,宾语从句和同位语从句都用that引导。There is no doubt that we will have an exam next week.I doubt whether/if Tom will recover.10
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 装配图网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。
