 Liferay权限管理
Liferay权限管理


《Liferay权限管理》由会员分享,可在线阅读,更多相关《Liferay权限管理(52页珍藏版)》请在装配图网上搜索。
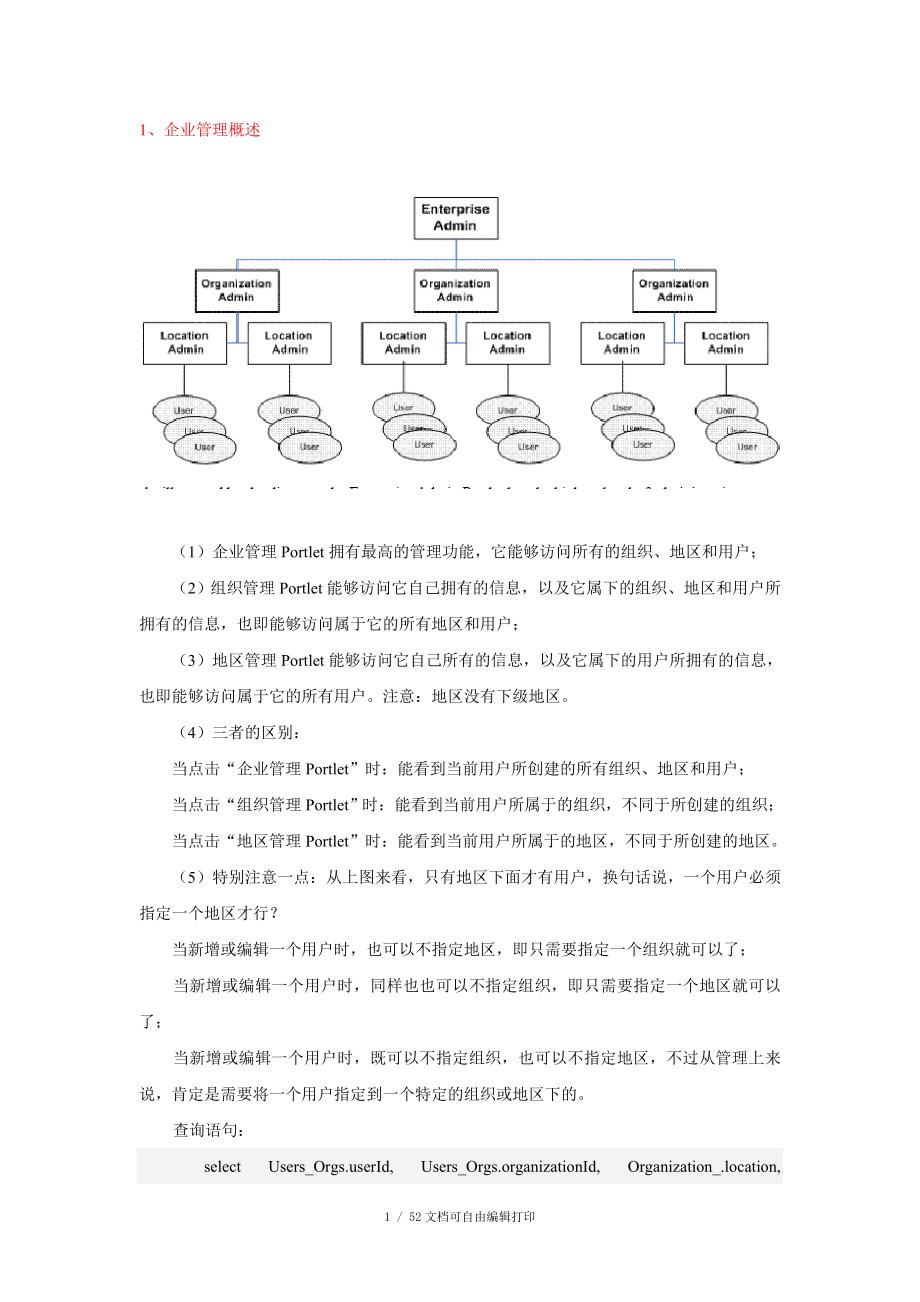
1、1、企业管理概述(1)企业管理Portlet拥有最高的管理功能,它能够访问所有的组织、地区和用户;(2)组织管理Portlet能够访问它自己拥有的信息,以及它属下的组织、地区和用户所拥有的信息,也即能够访问属于它的所有地区和用户;(3)地区管理Portlet能够访问它自己所有的信息,以及它属下的用户所拥有的信息,也即能够访问属于它的所有用户。注意:地区没有下级地区。(4)三者的区别:当点击“企业管理Portlet”时:能看到当前用户所创建的所有组织、地区和用户;当点击“组织管理Portlet”时:能看到当前用户所属于的组织,不同于所创建的组织;当点击“地区管理Portlet”时:能看到当前用户
2、所属于的地区,不同于所创建的地区。(5)特别注意一点:从上图来看,只有地区下面才有用户,换句话说,一个用户必须指定一个地区才行? 当新增或编辑一个用户时,也可以不指定地区,即只需要指定一个组织就可以了;当新增或编辑一个用户时,同样也也可以不指定组织,即只需要指定一个地区就可以了;当新增或编辑一个用户时,既可以不指定组织,也可以不指定地区,不过从管理上来说,肯定是需要将一个用户指定到一个特定的组织或地区下的。查询语句: select Users_Orgs.userId, Users_Orgs.organizationId, Organization_.location, Organization
3、_.namefrom Users_Orgs,Organization_where Users_Orgs.organizationId = Organization_.organizationIdorder by Organization_.location,Users_Orgs.userId图 (二)说明:这个图要说明的是:企业管理不是不指对某个企业的管理,同样组织管理和地点不是对某个组织,某个地点的管理。它的意义在于说明这是三个不同的等级,管理的范围也是有大有小的。其中企业管理是最大的范转,它可以利用整个系统下面的所有资源,而组织管理是次级的,它能利用的资源范围是在它的组织内部,它不能利用别
4、的组织的资源,组织下面的地点也是同样的。这仅仅是意义上的不同,名称完全可以更换。地点下面才是用户。如果用户被指派了Administrator角色,那么能够访问【Enterprise Admin】Portlet,否则不能访问该Portlet;在企业管理中可以对用户、组织、地点、用户组、角色进行维护,即增、删、改、查;通过角色定义权限,然后把角色指派给用户、社区、组织、地点、用户组;2、在Liferay中与管理有关的几个Portlet(1)Admin Portlet(2)Enterprise Admin Portlet(3)Organizations Admin Portlet(4)Locatio
5、ns Admin Portlet(5)Communities Admin Portlet3、组织和地区管理(1)组织和地区描述了一个企业的管理层次结构;(2)一个组织代表一个母公司,例如:Liferay USA;(3)一个地区代表一个母公司旗下的子公司,通常按照地理位置来区分,例如:Liferay Chicago、Liferay San Francisco ;(4)一个组织可以拥有任意多个地区;(5)一个用户且仅且只能属于一个组织和地区;(6)组织:湖南工业大学地区:湖南工业大学老校区湖南工业大学新校区湖南工业大学师专校区湖南工业大学冶金校区4、用户组管理(1)用户组不属于任何公司、任何组织、
6、任何地区,纯粹只是为了方便分配角色,为了方便分配权限,而将具有共性(比如:具有相同兴趣爱好等)的一些用户进行分组;(2)一个用户可以属于任意多个用户组;(3)用户组与用户组之间不存在从属关系,即用户组下面不能再分用户组。5、Portlet管理(1)在【Enterprise Admin】Portlet中,选中【Plugins】标签页,再选中【Portlets】标签页,如下图所示,从图中可以看出,每个Portlet所必须的角色。(2)编辑Portlet所必须的角色,如下图所示:(3)表Portlet主要功能:存储Portlet信息,当在【Enterprise Admin】Portlet中,对Por
7、tlet所必须的角色进行修改后,所必需的角色是指,只有当用户具有这些角色,才能对这个Portlet进行操作;字段:portletId PortletID;字段:roles 该Portlet所必需的角色;字段:active 该Portlet的活动状态;每个Portlet的初始化所必需的角色,存储在portlet-custom.xml中,如下所示:19Message Boardscom.liferay.portlet.StrutsPortletview-action/message_boards/view0text/htmlcom.liferay.portlet.StrutsResourceBun
8、dleprioritiesUrgent,/message_boards/priority_urgent.png,3.0Sticky,/message_boards/priority_sticky.png,2.0Announcement,/message_boards/priority_announcement.png,1.0ranksYoungling=0Padawan=25Jedi Knight=100Jedi Master=250Jedi Council Member=500Yoda=1000power-useruser6、Liferay Portal中的权限管理类似于面向对象编程中的类的
9、继承机制:例如:(1)现在有一个组织名为:湖南工业大学,它有三个子组织:湖南工业大学本部、湖南工业大学冶金校区、湖南工业大学师专校区;(2)父组织:湖南工业大学,它拥有三个地区:经管学院、计通学院、理学院;(3)子组织:湖南工业大学师专校区,它拥有一个地区:音乐系;(4)在此,父组织相当于一个超类,子组织相当于一个子类,子类将继承超类所拥有的全部成员变量和成员方法,子组织将继承父组织所拥有的全部地区;而子组织拥有自己新建的地区“音乐系”,父组织以及其他组织不具有“音乐系”。特别注意:对于用户,在此不适用于继承机制,因为一个用户只能属于一个地区和一个组织,不可以属于多个地区和多个组织,具有唯一性
10、,类似于类中的私有成员变量和成员方法,对于它的子类不可见。7、与权限有关的各实体定义与权限有关的实体包括:资源、权限、角色、用户、组织、地区、用户组、社区。Before using the new security model, an administrator must understand all the entities that compose the model. This chapter will define each of the entities and explain how they are related to the others.(1)ResourcesA reso
11、urce is a generic term for any object represented in the portal. Examples of resources include portlets (e.g., Message Boards, Calendar, Document Library, etc.), Java classes (e.g., Message Board Topics, Calendar Event, Document Library Folder, etc.), and files (e.g., documents, images, applications
12、, etc.). Resources can have one of three types of scope enterprise, community, or individual. The diagram below shows how these types are related.Essentially, an enterprise is the umbrella grouping for all objects within the portal. A resource that has enterprise scope applies to all objects of that
13、 type in the company. For example, a Message Board Category resource with enterprise scope encompasses every topic across all communities and all message boards within the enterprise. An enterprise can contain any number of communities. A resource that has community scope only applies to the objects
14、 within a particular community. For example, assume that the “Developer community has several message boards. A Message Board Category resource with “Developer community scope would encompass all category within the “Developer message boards. Each community can contain any number of objects. A resou
15、rce that has individual scope only applies to a single object. For example, assume that the “Developer community has a message board that contains the topic “Java Issues. A Message Board Category resource withindividual scope would have a one-to-one correlation with the “Java Issues topic.(2)Permiss
16、ionsA permission is defined as an action acting on a resource. The table below gives some example permissions related to message board topics.Example PermissionsEnterprise and community scoped permissions can only be assigned to entities (e.g., users, communities, organizations, and locations) via r
17、oles. See section 2.3 for more details. Individual scoped permissions can be assigned to a user, community, organization, location, or guest. If a permission is assigned to a community, organization, location, or guest, then all users that are members of that entity receive that permission.In genera
18、l, permissions are additive. Therefore, a user could receive all three of the permissions in the table above even though they are all of different scope. Consider a situation where a view “Java Issues” permission of individual scope was assigned directly to a user and a view Message Board Category p
19、ermission of enterprise scope was assigned to the same user through a role (see section 2.3 for more information on roles). Because permissions are additive, the user could receive the view permission for the “Java Issues” category from either the individual or enterprise scope. However, permissions
20、 are always checked in the following order: Individual Community EnterpriseTherefore, as soon as the system finds the view permission of individual scope, it stops checking and gives the user permission to view. However, also consider the case where the individual scope permission is removed from th
21、e user. Now when the system checks, it will not find an individual scope or community scope permission, but it will find the enterprise scope permission. For an administrator, this situation can often lead to a great deal of confusion a permission is removed from one entity, butthe permission is sti
22、ll derived from another entity. As a rule of thumb, if an administrator ever removes a permission from an entity, yet user(s) still has the permission, the administrator should look for derived permissions in the system.(3)RolesA role is a collection of permissions. As such, a role serves no purpose
23、 unless permissions are assigned to it. An example role might be a “Message Board Administrator. The role might be assigned permissions to View, Update, and Delete Message Board category resources that have company scope.Ultimately, a user assigned the “Message Board Administrator role would be able
24、 to view, update, and delete any topic for any message board in the company. Roles can be assigned to a user, community, organization, or location. If a role is assigned to a community, organization, or location, then all users that are members of that entity receive the role.(4) UsersA user is an i
25、ndividual who performs tasks using the portal. Depending on what permissions and roles that have been assigned, the user either has permission or does not have permission to perform certain tasks. Before logging in to the portal, a user is considered a guest. Guests have their own set of default per
26、missions for objects in the portal, but even these can be customized by administrators. After logging in to the portal, a user is considered a registered user. Registered users can receive permissions in the following ways: Permission is directly assigned to the user Permission is assigned to a comm
27、unity that the user belongs to Permission is assigned to an organization that the user belongs to Permission is assigned to a location that the user belongs to Permission belongs to a role that is directly assigned to the user Permission belongs to a role that is assigned to a community that the use
28、r belongs to Permission belongs to a role that is assigned to an organization that the user belongs to Permission belongs to a role that is assigned to a location that the user belongs to(5) Organizations and Locations Organizations and locations represent a corporate hierarchy. An organization repr
29、esents a parent corporation. An example would be Liferay USA. A location represents a child corporation of an organization, often times distinguished by its geographic location. Organizations can have any number of locations. Example locations of the Liferay USA organization might be Liferay Chicago
30、, Liferay SanFrancisco, and Liferay Los Angeles. A user can only belong to a single organization and location.Both roles and individual permissions can be assigned to organizations and locations. By default, locations inherit permissions from their parent organization. Going back to the example abov
31、e, if the “Message Board Administrator role is assigned to the Liferay USA organization, then all members of the Liferay Chicago, Liferay San Francisco, and Liferay Los Angeles locations would inherit thepermissions associated with the role.(6) CommunitiesA community is a grouping of users by intere
32、st or skill set. For example, a “Pet Lovers community would consist of users who have an interest in their pets, while a “Tech Support community would consist of users who have the skills to provide technical support to an organization. A user can belong to any number of communities. NOTE: In previo
33、us versions of Liferay, communities were called groups. As far as permissions are concerned, communities are not specific to any organization or location. Both roles and individual permissions can be assigned to communities.(7) UserGroupsA user group is a grouping of users. Unlike organizations, loc
34、ations, and communities, user groups have no context associated with them. They are purely a convenience grouping that aids administrators in assigning permissions and roles to a group of users instead of individual users or assigning a group of users to a community. A user can belong to any number
35、of user groups. Both roles and individual permissions can be assigned to user groups, and every user that belongs to that user group will receive the role or permission.权限分配是在资源的基础上进行分配的。要理解权限的分配,首先要理解什么是资源。在系统里面,一个portlet是资源,这是对资源粗的划分,还有就是一个portlet具有什么的功能,比如高级文章编审这个portlet具有编辑和审批的功能。我们就可以把这个功能当作资源,
36、分配相应的权限给用户。权限的定义:所谓的权限是定义在某个资源上的操作动作(比如:高级文章编审这个portlet资源中的编辑)角色的定义:角色是权限的组合(也就是说一些资源的权限的组合起来,形成一个权限集合,我们把这个集合叫做一个角色)。用户的定义:用户就是执行某些操作完成某些任务的人。用户之所以能完成某些操作,依赖给用户分配的角色和权限。具有某个角色和权限,他就具有了某些操作的功能。在没有登录系统之前,所有的用户都被当作是一个Guest。Guest用户具有某些默认的权限。分配权限的方式有以下几种:1、 权限(角色)直接分配给用户。2、 权限(角色)分配给用户所在社区。3、 权限(角色)分配给用
37、户所在的组织。4、 权限(角色)分配给用户所在的地区。资源的定义:资源Portlet资源Model资源示例:Message Boards CategoryCategory文件资源示例:documents8、层次关系的比较:(1)角色之间不存在层次关系,这与一般RBAC中所提及的角色结构不一样,在一般RBAC中,角色之间有层次关系;(2)组织之间存在层次关系;(3)地区之间不存在层次关系;(4)用户组之间不存在层次关系;9、在分配权限之前必须要弄清楚几个问题?(1)分配给谁?角色、社区、组织、地区、用户组、用户(2)权限来源于哪里? 要搞清权限来源于哪里,即要知道permissionId是什么,
38、就要知道resoureceId和actionId是什么? 权限可以分为静态的权限和动态的权限。静态的权限:指系统预定义的权限,这来源于xml文档;在权限开发中有DRAC四个步骤,其中第二步就是注册权限,将xml文档中配置好的权限保存到数据库中。动态的权限:在系统运行过程中,或者说在使用系统的过程中,进行权限分配后,产生的权限。例如:给角色SupportMBAdmin,对Portlet资源Message Boards Portlet,添加Add Category操作后,就会在Permissions_表中新增一条记录。(3)actionId来源于哪里?对资源的所有操作信息,来源于xml文档(4)r
39、esourceId来源于哪里?资源也可以分为静态的资源和动态的资源。静态的资源:指系统预定义的资源,这来源于xml文档,类似于静态的权限。动态的资源:在系统运行过程中的产生的资源。例如:增加一个社区、增加一个页面、增加一个栏目、增加一篇文章等,都会在Resource_表中增加相应的记录。10、二次开发指南中的权限介绍Liferay Portal采用:用户用户组角色Portlet的关联方式来实现用户权限的管理用户:隶属于用户组(也可以单独存在);用户组:具有某种(多种)角色;用户组是对具有相同角色的用户的聚合,只要把用户需要的角色赋给用户组,则该用户组内所有的用户都具有了该角色,具有该角色的所有
40、权限,这样子就简化了用户权限管理;角色:分配给用户组,也可以直接分配给用户;Portlet:操作某个Portlet需要具有其指定的角色。11、如何对单个Portlet进行权限控制例如【Admin】、【Enterprise Admin】、【Organization Admin】、【Location Admin】、【Communities】、【Message Boards】portlet等?选择一个Porlet,再选择顶部工具栏的【Configure】按钮;选择【Permissions】标签页,即可对该Portlet进行权限控制;选择【Users】标签页,选择一个用户,在此选择【Test DLC
41、1】,如下图所示:点击【Update Permissions】,即可将相关权限分配给所选择的用户,如下图所示,从图中右边可以看到对Resource:Message Boards Portlet,可选的Actions有:Add Category(添加栏目/类别)、Ban User()、Configuration(配置该Portlet)、View(查看该Portlet)。12、如何对一个Portlet下的各资源进行权限控制例如【Organization Admin】portlet下的组织,【Location Admin】下的地区,【Communities】下的社区,【Message Boards】
42、下的Category和Messages等? 选择一个Porlet下的资源,例如选择【Organization Admin】portlet下一个组织【Liferay, Inc】,点击【Actions】,选择【Permmissions】,即可对当前所选的资源的进行权限控制。13、对资源(Portlet资源或者Mode资源)的初始化操作存储在哪里?下面是messageboards.xml,Message Boards Portlet的配置文档。19ADD_CATEGORYBAN_USERCONFIGURATIONVIEWVIEWVIEWADD_CATEGORYcom.liferay.portlet.
43、messageboards.model.MBCategory19ADD_CATEGORYADD_ADD_MESSAGEDELETEPERMISSIONSREPLY_TO_MESSAGESUBSCRIBEUPDATEUPDATE_THREAD_PRIORITYVIEWADD_ADD_MESSAGEREPLY_TO_MESSAGESUBSCRIBEVIEWVIEWADD_CATEGORYADD_SUBSCRIBEUPDATEUPDATE_THREAD_PRIORITYcom.liferay.portlet.messageboards.model.MBMessage19DELETEPERMISSIO
44、NSSUBSCRIBEUPDATEVIEWSUBSCRIBEVIEWVIEWSUBSCRIBEUPDATE(1)定义了Portlet资源的操作(Actions),如下图所示:(2)定义了模型资源的操作(Actions),如下图所示:(3)定义了社区对当前资源默认具有的操作,意即默认情况下,在这个社区(组)中Portlet有什么样的行为,以另外一种方式来说,一个用户在最低程度上访问这个社区时能做什么呢? 同样地, 标签 定义了当一个客人访问到包含这个portlet的版面时,哪些行为默认是允许的. 所以如果一个访客可以访问到包含公告板portlet的社区页时,访客应该在最低程度上, 根据messa
45、geboards.xml文件的定义, 就能够浏览这个portlet(对portlet中的内容并不是必须的).否则,访客就会在portlet中看到一个错误信息.例如对Message Boards Category,如下图所示:com.liferay.portlet.messageboards.model.MBCategoryADD_ADD_MESSAGEREPLY_TO_MESSAGESUBSCRIBEVIEWVIEWADD_CATEGORYADD_SUBSCRIBEUPDATEUPDATE_THREAD_PRIORITY14、权限的设计、管理和开发(1)权限设计一、权限设计的基本理念:RBAC
46、基于角色的访问控制;ORBAC基于组织机构和角色的访问控制;二、Liferay中的权限设计思想;三、其他系统中的权限设计思想:OA系统、门户网站:暨南大学、人大等。(2)权限管理一、创建权限;二、分配权限;三、使用权限。(3)权限开发15、Role Permissions(1)Assigning Company Permissions to a RoleGoal: To assign a permission to the “MB Category Admin role that allows users to view any message board category in the co
47、mpany (i.e., action = View, resource = Message Board Category, scope = Company).详细过程请参考:liferay_4_portal_administration_guide第47页:给角色SupportMBAdmin分配权限:资源:Message Boards Portlet操作:Add Category scope = 1Ban User scope = 1Configuration scope = 1View scope = 1企业级作用范围测试:Before:以用户test.lax.1登录系统,进入My Com
48、munity 1社区,从下图中可以看到,在Message Boards Portlet中不能进行如下操作:Add Category、Ban User、Configuration、View。以用户test.lax.1登录系统,进入My Community 2社区,从下图中可以看到,在Message Boards Portlet中不能进行如下操作:Add Category、Ban User、Configuration、View。After:以用户test.lax.1登录系统,进入My Community 1社区,从下图中可以看到,在Message Boards Portlet中现在能进行如下操作:
49、Add Category、Ban User、Configuration、View。以用户test.lax.1登录系统,进入My Community 2社区,从下图中可以看到,在Message Boards Portlet中现在能进行如下操作:Add Category、Ban User、Configuration、View。(2)Assigning Community Permissions to a RoleGoal: To assign a permission to the “MB Category Admin role that allows users to view any mess
50、age board category in the company (i.e., action = View, resource = Message Board Category, scope = Company).详细过程请参考:liferay_4_portal_administration_guide第49页:给角色SupportMBAdmin分配权限:资源:Message Boards Portlet操作:Add Category scope = 2 community = community 1Ban User scope = 2 community = community 1Conf
51、iguration scope = 2 community = community 2View scope = 2 community = community 2社区级作用范围测试:Before:以用户test.lax.1登录系统,进入My Community 1社区,从下图中可以看到,在Message Boards Portlet中不能进行如下操作:Add Category、Ban User、Configuration、View。以用户test.lax.1登录系统,进入My Community 2社区,从下图中可以看到,在Message Boards Portlet中不能进行如下操作:Add
52、 Category、Ban User、Configuration、View。After:以用户test.lax.1登录系统,进入My Community 1社区,从下图中可以看到,在Message Boards Portlet中现在能进行如下操作:Add Category、Ban User,但是还是不能进行如下操作:Configuration、View。以用户test.lax.1登录系统,进入My Community 2社区,从下图中可以看到,在Message Boards Portlet中现在能进行如下操作: Configuration、View,但是还是不能进行如下操作:Add Category、Ban User。16、Community Permissions(1)Community Portlet PermissionsGoal: To understand the concept of a Community Admin and how a Community Admin can further delegate permissions to members of the community.详细过程请参考:liferay_4_por
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 装配图网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。
相关资源
更多 2022年03月2022年江苏无锡市惠山区教育局选聘优秀青年人才46人公开练习模拟卷(第5次)
2022年03月2022年江苏无锡市惠山区教育局选聘优秀青年人才46人公开练习模拟卷(第5次)
 精华德育工作计划模板汇编7篇
精华德育工作计划模板汇编7篇
 2022年01月安徽省太湖县江塘乡关于公开招考乡村振兴专干公开练习模拟卷(第9次)
2022年01月安徽省太湖县江塘乡关于公开招考乡村振兴专干公开练习模拟卷(第9次)
 广东中山大学附属口腔医院消毒供应中心工勤人员招考聘用2人模拟卷(内含100题)
广东中山大学附属口腔医院消毒供应中心工勤人员招考聘用2人模拟卷(内含100题)
 瓦斯抽采系统设计
瓦斯抽采系统设计
 大学生创业文化工作室室策划书复习过程
大学生创业文化工作室室策划书复习过程
 广东省嘉应学院2021年招聘台湾地区高层次人才模拟卷(内含100题)
广东省嘉应学院2021年招聘台湾地区高层次人才模拟卷(内含100题)
 2022年03月广东深圳市光明区应急管理局特聘专干选聘1人公开练习模拟卷(第9次)
2022年03月广东深圳市光明区应急管理局特聘专干选聘1人公开练习模拟卷(第9次)
 四川农业大学21春《盆景制作与鉴赏》在线作业二满分答案42
四川农业大学21春《盆景制作与鉴赏》在线作业二满分答案42
 2022年02月中国水利水电科学研究院减灾中心招考聘用公开练习模拟卷(第8次)
2022年02月中国水利水电科学研究院减灾中心招考聘用公开练习模拟卷(第8次)